
The power supply circuit plays an important role in every electrical and electronic circuit to supply power from the owl circuit to the computer and various machines. This type of load requires different forms of power over different ranges and characteristics. Therefore power is converted to the desired form using different types of power converters.
Mainly works with different loads such as SMPS, AC power supply, AC to DC power supply, programmable power supply, high voltage power supply, and uninterruptible power supply. In today’s article, we will talk about what SMPS is and what is its working principle, and much more about it.
What is SMPS (Switch-Mode Power Supply)?
The full name of SMPS is Switch-Mode Power Supply. SMPS is defined in simple language when the need for electricity comes in the form of a switch. In which electrical energy is converted from one form to another with essential properties called SMPS. This power is used to obtain a regulatory DC input voltage from DC output or uncontrollable AC for power. SMPS is just as complex as any other power supply system. This is a power source used for loading.
SMPS is an important device for a wide variety of electrical and electronic devices. Which provides it with a source of power consumption specifically designed for electronic projects.
Topologies of SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply):
The topology of SMPS is classified into different types which are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Topologies of SMPS |
| #1. | AC-DC converter |
| #2. | DC-DC converter |
| #3. | Fly-back Converter |
| #4. | Forward Converter |
Working Principle of SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply):
The working principle of switch-mode power supply topologies is as follows:
#1. AC-DC Converter SMPS Working:

In this type of SMPS, the input supply is AC and in the output, we get a DC supply. Rectifiers and filters are used to convert this AC power to DC. This uncontrollable DC voltage is given to the affected power factor correction circuits. This is because there is a low current pulse inside the rectifier around the peak of the voltage.
This includes high-frequency energy which influences to reduce of the power factor. This is due to power conversion but we have used AC input instead of DC input supply. Therefore, a combination of rectifier and filter, this block diagram is used to convert AC to DC, and switching an operation is done using a power muffle amplifier.
MOSFET transistors use low resistance and are capable of resisting high currents. The switching frequency is chosen so that normal humans (above 20KHz) must be kept low and the operation of the switch is controlled using a PWM oscillator.
Again this AC voltage is given to the output of the transformer as shown in the figure or the voltage level goes down. After that, the output of this transformer is fixed and smoothed using the Output filter and corrector. The output voltage is controlled by the reaction circuit compared to the reference voltage.
Also Read: What Is an Induction Motor | Types of Induction Motor | Advantage of Induction Motor
#2. DC-DC Converter SMPS Working:

The input supply of this power source is taken from the high-voltage DC power directly from the DC power source. This high-voltage DC power source is then reduced to 15KHz-5KHz. It is then fed to a 50 Hz step-down transformer unit.
The output of this transformer is the input of the rectifier and the output of the rectifier is the power used as the source of loads. The oscillator is controlled on time and a closed-loop regulator is formed.
The switching power supply output is regulated using the pulse width modulation shown in the circuit above, the switch is operated with the help of a PWM oscillator. The power is then indirectly controlled with the help of a step-down transformer when power is supplied to the transformer.
Therefore, the output pulse width is controlled by modulation, as these output voltages and the PWM signal are proportional to each other.
If the duty cycle is 50%, the maximum power is transferred by the transformer, and if the duty cycle is reduced, then the power of the transformer is also reduced by reducing the interruption.
Also Read: What is a Voltage Regulator | Types of Voltage Regulator | Working of Voltage Regulator
#3. Fly-Back Converter Type SMPS Working:

Any SMPS whose output power is less than 100W is known as a fly-back converter SMPS. Compared to other SMPS, the circuit of these SMPS is simple and straightforward. This type of SMPS is used for low power consumption.
The uncontrolled input voltage of constant intensity is switched to the preferred output voltage by switching using MOSFET; The frequency of switching is around 100 kHz. Voltage isolation is achieved using a transformer. The operation of the switch can be controlled using PWM while operating a practical fly-back converter.
The fly-back transformer shows special characteristics compared to a normal transformer. The fly-back transformer consists of two windings that act as magnetically connected inductors.
The output of this transformer is distributed by capacitors and diodes for the improvement of filtering. The output of SMPS can be taken as the voltage across the filter capacitor as shown in the figure.
Also Read: What is Limit switch | Working Principle Of Limit switch | Application of Limit switch
#4. Forward Converter Type SMPS Working:
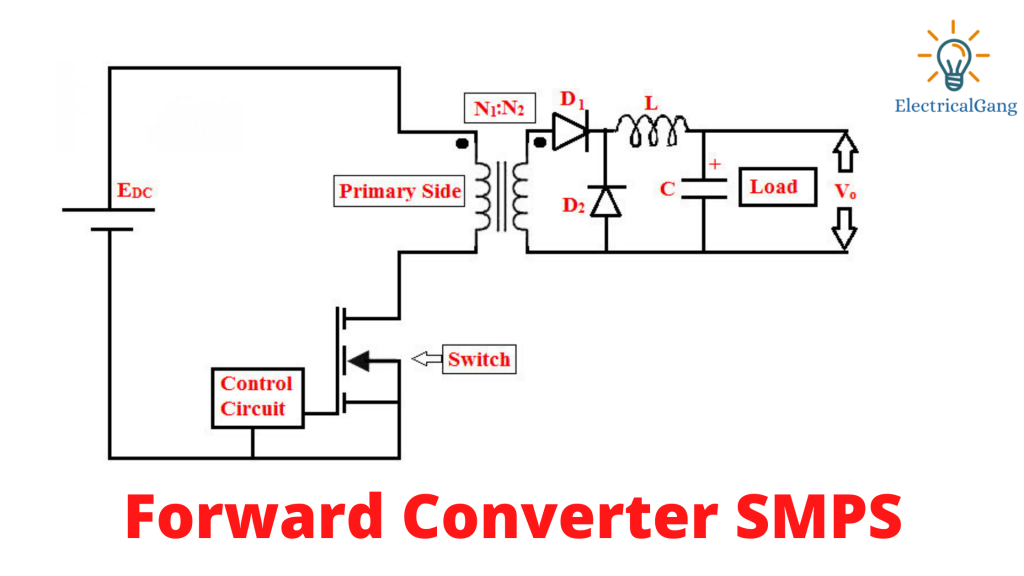
The design of this type of SMPS is almost the same as the flyback converter type SMS. In such SMPS the switch is connected to the output of the secondary winding of the transformer to control. Compared to a flyback converter, the filtering and correction circuit is more complex. These SMPS are also known as DC-DC buck converters and are also used for scaling and isolation of transformers.
In addition to the D1 “diode and” C “capacitor, an inductor L and diode D are connected at the end of the output. If the ‘S’ switch operates, then the primary winding of the input transformer is turned off. Therefore, a fixed voltage is generated on the transformer-developed secondary winding. So diode D 1 becomes forward biased and the voltage scaled by the load moving LPF passes
When switch S is turned on, the current through the winding reaches zero. The current cannot be changed anytime soon by refreshing filters and loads and this current is offered a lane by diode D2 along the coast. Using a filter inductor, the required voltage and electromagnetic force towards the D2 diode become necessary to influence the stability of the current.
Even if the current is falling against the output voltage, an almost constant output voltage can be maintained with the existence of a large capacitive filter. It is used regularly for various switching applications with a power range from 100 W to 200 W.
Advantages of Smps:
The benefits of SMPS are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Advantages of Smps |
| #1. | High efficiency |
| #2. | Compact |
| #3. | Costs |
| #4. | Flexible Technology |
#1. High efficiency:
The main advantage of SMPS is that it is more efficient than linear regulators. This is because the switching transistor dissipates a little power when it acts as a switch.
#2. Compact:
Forms SMPS can be made more compact as a result of higher efficiency and lower levels of heat dissipation.
#3. Costs:
Switch mode is the value of a point making the power supply. Efficiency The high efficiency and switching nature of the design means that the standby power loss is often lower than that of transformers and this reduces costs.
#4. Flexible Technology:
The SMPS feature can be used to provide high-efficiency voltage conversion to voltage step-up or “boost” applications or to step-down “buck” applications.
Applications of SMPS:
The application of SMPS is as follows:
- The most common use of this is in computers.
- Smps is used in security systems.
- This is used in the railway system.
- It is also used in battery chargers.
- It is also widely used in machine tool industries.
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

What is the main function of SMPS?
SMPS is a switch-mode power supply. A type of high-frequency power conversion device and abbreviation for power supply device. Its function is to convert the required voltage or current level by various forms of architecture.
How does a switch power supply work?
SMPS works by turning the main power on and off at a high speed to reduce the voltage. In such a case the reduction in voltage depends on the ratio of time and off time. Switching happens very quickly, 10,000 times or faster per second.
What is SMPS’s short answer?
SMPS stands for Switch-Mode-Power-Supply. It is used in all types of computers. Today’s modern computers have an SMPS that takes the improved AC input power from the board in the house, by making a power factor correction and then converting the output to a single or lower voltage DC output.
What are SMPS Applications?
The application of SMPS is as follows:
- The most common use of this is in computers.
- Smps is used in security systems.
- This is used in the railway system.
- It is also used in battery chargers.
- It is also widely used in machine tool industries.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
thank you