
An overload relay is an electrical device used to protect an electric motor from overheating. There must be adequate motor safety. The electric motor can be operated safely with the help of an overload relay, fuse, or circuit breaker. But this relay provides protection to the motor. When a circuit breaker or fuse protects the circuit.
More purposefully, the fuse, as well as the circuit breaker, are designed to detect the overcurrent inside the circuit. The relay is designed to detect overheating when the electric motor is heated. For example, an overload relay can be explored without tripping the CB (circuit breaker). One does not restore the other. In today’s article, we will discuss the type of overload relay and its overview.
What is an Overload Relay?
Definition: An overload relay can be defined as something that is an electrical device designed primarily to mimic a heating prototype of an electric motor. As well as when the heat detection device in the relay receives a fixed temperature it breaks the current.
The design of the overload relay can be done with the heater. Which usually has a closed connection. When the heater gets too hot it is unlocked. The connection of this relay is made in series and placed between the motor and the contactor to prevent the motor from restarting during overload.
Connection Diagram of Overload Relay:
The connection diagram of the overload relay is shown below and the connection of the overload relay symbol looks like two opposite question marks otherwise the overload relay function like the ‘S’ symbol is discussed. Although there are many types of overload relays available in the market, the most widely used rally in the market is the “bimetallic thermal overload relay”.
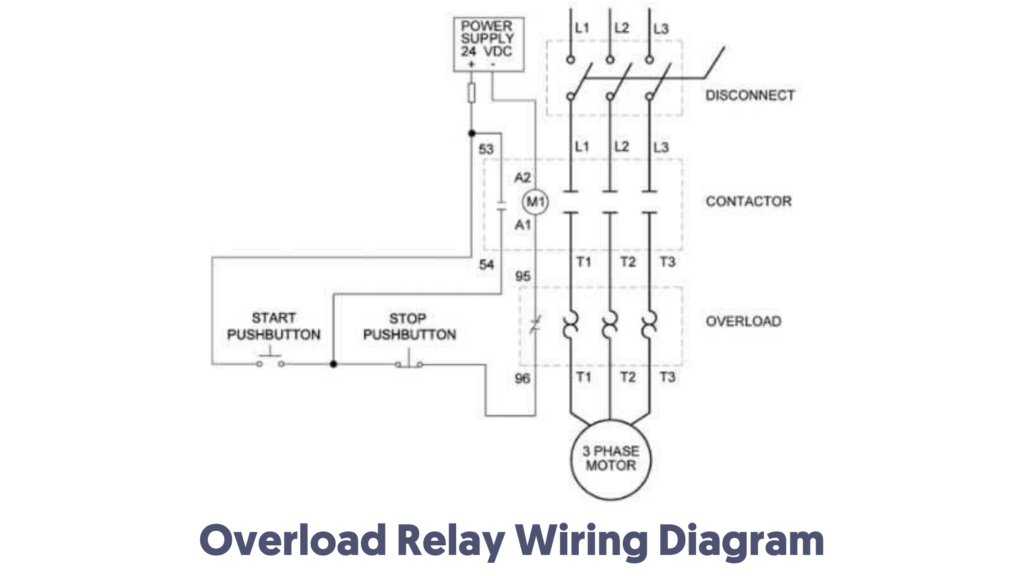
The design of this relay uses two different types of metal strips and these straps can be interconnected as well as expand at different rates when heated. When this strip is heated to a certain temperature then this strip can give enough turns to break this circuit.
Whenever the flow to the motor is higher than what is charged for the heater, the overload is detected after a few seconds. The class of overload relays is classified into three types based on the duration of the relay exploration. The Class 10, Class 20, and Class 30 overload relays can be found corresponding to 10 seconds, 20 seconds, and 30 seconds.
The main feature of this relay is that it prevents the motor from starting immediately. For example, the overload relay explores into the bimetallic relay, then the NC (normally closed) bimetallic connections will unlock the circuit until this strip cools. If any contactor tries to push the start switch to turn off the switch, the motor will not start.
Suggested Read: How to Solve LG Content Store Not Working Problem?
Overload Relay Working Principle:
The working principle of an overload relay depends on the electro-thermal properties within the bimetallic strip. In a motor circuit, this is designed in such a way that current can flow through its poles in a motor. When the current exceeds the set value the bimetallic bar starts to heat up and then it turns
These relays are always taken in the same work with the contactor. Once the bimetallic strip is heated the contactor trip is activated and the electric current flowing towards the contactor coil is broken and deactivated and stops the flow to the motor.
The time taken for tripping is always proportional to the flow of the whole relay. This is why this relay is known as current dependent as well as the inversely time-delayed relay.
This relay is always connected in series to the motor so that the current flows towards the motor. When the motor is activated then the motor flowing during OLR will be there. This will trip to a fixed level once the surplus current passes through the relay. That is why the circuit will open between the power source as well as the motor.
This relay can be reset automatically or manually after a pre-adjusted time. Once the overload is detected and the same is done, the motor will start working again as before.
Parts of Overload Relay:
The overload relay uses a part other than the bimetallic strip which is as follows:
| Sr. No. | Parts of Overload Relay |
| #1. | Terminal |
| #2. | Ampere Range Setting |
| #3. | Reset Button |
| #4. | Auxiliary Contact |
| #5. | Test Button |
#1. Terminal:
The input terminals are shown with L1, L2, and L3 which are directly connected to the contactor as shown in the figure of the relay. The motor supply can be connected to T1, T2, and T3 terminals.
#2. Ampere Range Setting:
A knob is available on the OLD that can be used to set the current flow to the motor. The current can be set to the upper and lower limits provided. An additional knob is also provided for class selection tripping in electronic OLD.
#3. Reset Button:
This button is located on the OLD and is used to reset the relay after the trip and fault clearance.
Manual or Auto-Reset Selection Button:
Using this button one can manually select and automatically reset the relay after the trip. Once the device is ready for auto-reset then a remote reset of the relay can be obtained
#4. Auxiliary Contact:
Two auxiliary contacts are used in this relay. Such as one NO contact and another NC contact. NC contact is not used when disconnecting the trip signal and contactor. NC contacts contactor coils are capable of direct switching.
#5. Test Button:
The test button is used to check the control wiring.
Suggested Read: Electrical Substation Components And Their Workings
Overload Relay Types:
Overload relays are classified into two main types one is thermal overload relays and the other is magnetic overload relays.
| Sr. No. | Types of Overload Relay |
| #1. | Thermal Overload Relay |
| #2. | Magnetic Overload Relay |
| #3. | Bimetallic Thermal Overload Relay |
| #4. | Electronic Overload Relay |
| #5. | Fridge Overload Relay |
#1. Thermal Overload Relay:

A thermal-type relay is a protective device. And this is mainly designed to cut power. When the motor uses excessive current for an extended period of time. To achieve this, the relay involves an NC relay. Once a maximum current is supplied to the motor circuit, the relay opens due to the modified temperature of the motor relay, otherwise, it detects the overload current depending on the type of relay.
This relay relates to the circuit breaker as well as its application in construction. However, most circuit breakers disrupt the circuit. This motor is evenly designed to calculate the heating profile if the overload occurs even for a moment. Thus the circuit should be overloaded for the entire period before it breaks. Thermal overload is classified into two types of solder pot as well as a bimetallic strip.
#2. Magnetic Overload Relay:

The magnetic overload relay is operated by finding the strength of the magnetic field. Which is generated by the flow towards the motor. This can be made from a variable magnetic core inside the relay coil that holds the motor current. The arrangement of the current inside the coil pulls the core. As the core rises too much it then trips the set of attachments to the apex of the relay.
The main difference between a thermal overload relay and a magnetic relay is that the magnetic relay does not respond to the ambient temperature. This relay is usually used in an area where extreme changes in ambient temperature are displayed. Magnetic overload relays are classified into two types, electronic well as dashpot.
#3. Bimetallic Thermal Overload Relay:
The function of this thermal overload relay depends mainly on the heating property of the bimetallic strip. Direct heating is used to supply full current to the motor using an overload relay, also known as an OLR. As a result, it gets heated due to direct current flow.
In case of no direct heat, the strip can be adjusted in close contact with the conductor in the relay. The current flows towards the electric motor and is heated by a bimetallic strip. Thus the conductor will be insulated so that no current flows across the strip.
Suggested Read: Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping Without Load | How to Stop Tripping Without Load
#4. Electronic Overload Relay:
Another name for Electronic Overload Relay is Solid-State Overload Relay. This type of relay does not include a bimetallic strip in the interior. As an alternative, it uses a current transformer to calculate the sum of the current flowing to the motor. Or temperature sensor. This type of relay microprocessor-based technique is used for security.
Here the PTC plays a key role in detecting the temperature once an overload error has occurred as well as tripping the circuit. Some overload relays come with Hall Effect sensors as well as a current transformer to detect direct current flow.
The main advantage of an Electronic Overload Relay compared to a thermal overload relay is that it lacks a bimetallic strip resulting in less heat in the relay. Also, this type of relay is more accurate than a thermal relay.
Electronic overload relays are used where the start and stop of the motor are frequently required. These relays can be designed to withstand the initial flow of the motor for a restricted period.
#5. Fridge Overload Relay:
Protection devices such as overload relays are also used in the compressor circuit of refrigerators. Power is supplied to the winding of the compressor motor using an overloaded machine. This type of relay is mainly used to accommodate the starting winding inside the circuit. Unless the compressor is at running speed.
Suggested Read: The Ultimate Guide to Fixing Hisense TV Problems
How does an OLR Guard from Phase Failures?
In the normal operation of an OLR, the current flow on each pole of the electric motor remains the same for a period of time. If a phase is interrupted for some reason then the current flow in the remaining two phases increases to a normal value. So the relay heats up and trips. Phase failure is also called phased loss otherwise single facing of the motor.
These relays will not be able to protect against short circuit currents but must be used by short circuit protection devices to protect them. Or any short circuit inside the electric motor can easily damage it. This relay can prevent phase loss, phase imbalance, and overload, but not short circuits.
What Causes the OLR Trip?
There are three main reasons why an OLR trip may occur:
- Motor overload.
- Input phase loss.
- Phase imbalance.
And there are some additional security features available but vary from one designer to another.
Overload Relay Tripping:
The time used to unlock the contactor during overload is displayed through the trip class. Usually, these are divided into different categories like 5, 10, 20, and 30. This relay travels towards the electric motor at full load current in 5 seconds, 10 seconds, 20 seconds, and 30 seconds.
Commonly used overload relays are class 10 and 20 while class 30 OLR is mainly used to protect motors while handling high inertia loads. Class 5 types of relays are mainly used for motors that require extremely fast tripping.
Motor Overload Relay:
Overload relays are part of the motor starter (assembly of contactor plus overload relay). They protect the motor by monitoring the current flowing in the circuit. The overload relay can be reset manually, and some overload relays will reset automatically after a certain period of time.
Overload Protection Relay:
Overload protection relays prevent motor damage by monitoring the current in the motor circuit and breaking the circuit when an electrical overload or a phase failure is detected. Since relays are much cheaper than motors, they provide an affordable way of protecting motors.
Eaton Overload Relay:
Eaton offers a wide range of overload relays to provide full motor protection. The overload relay types include fixed bi-metallic, interchangeable heater bimetallic, and electronic. Flexible mounting ensures that they can be installed on a contactor, panel, or separate enclosure.
Electronic Overload Relay:
Electronic overload relays offer reliable and precise protection for motors in the event of overload or phase failure. The electronic overload relay can make up a compact starting solution together with contactors. Main benefits. Reliable protection for motors. Easy to create starters.
Applications of Overload Relay:
Some of the applications of Overload Relay are as follows:
- This main curry is used extensively for motor safety.
- This can be used to detect an overload condition as well as a defective condition. And then announces trip commands for the protective device.
- These relays have evolved into microprocessor systems as well as solid-state electronics.
- This relay deactivates the device whenever an extreme current is drawn.
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

How does overload relay work?
An overload relay identifies and protects the current flowing in the motor. When the current is high for a longer period of time the heater opens the relay contact which is in the contact coil in the current. When the contact opens the contactor coil de-energizes, resulting in a malfunction of the main power in the motor.
What are the two basic types of overload relays?
Overload relays are classified into two main types one is thermal overload relays and the other is magnetic overload relays.
What is the main function of an overload relay?
The overload protection relay monitors the current in the circuit of the motor while preventing damage to the motor by breaking the circuit against a problem like an overload or phase loss. Since relays are much cheaper than motors, they offer an inexpensive way to secure motors.
What is the difference between a circuit breaker and an overload relay?
A relay is a switching device that signals a circuit breaker as soon as a fault occurs in the power system. The circuit breaker automatically breaks the circuit when a signal is received from the relay. The relay cannot break contact.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –
Hi,
Your article is very informative and has deep information about overloadrelays and types. Thanks for sharing such a great article would love to see more kind of blogs like this.
Thank you
Thanks alot
Thank you for yours effort to spread the knowledge of industrial application of electrical engineering .
Thank you