
The insulator is used to prevent leakage from the overhead line and the current coming toward the earth. The insulator is overhead and not installed on end. The overhead plays a very important part in the transmission line. Insulators can be made from a variety of materials, such as rubber, wood, plastic, and mica.
Insulators used in electrical systems are mainly made of materials like glass, ceramic, steatite, PVC, and polymer. But the most common material used in the manufacture of insulators is porcelain. In today’s article, we will talk about how many types of insulators there are.
Suggested Read: What are Conductors and Insulators
Types of Electrical Insulators:
Insulators are classified based on their rating and are mainly used for transmission lines. The types of insulators are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types of Electrical Insulators |
| #1. | Pin Insulator |
| #2. | Shackle Insulator |
| #3. | Post-Insulator |
| #4. | Suspension Insulator |
| #5. | Strain Insulator |
| #6. | Stay Insulator |
| #7. | Disc Insulator |
#1. Pin Insulator:

Pin-type insulators are used extensively in distribution lines. The voltage capacity of a single insulator disc is up to 11 kV. It is designed to have more mechanical strength. The distribution line can be adjusted horizontally or vertically. These are easier to construct than other insulators and require less maintenance than other insulators.
#2. Shackle Insulator:
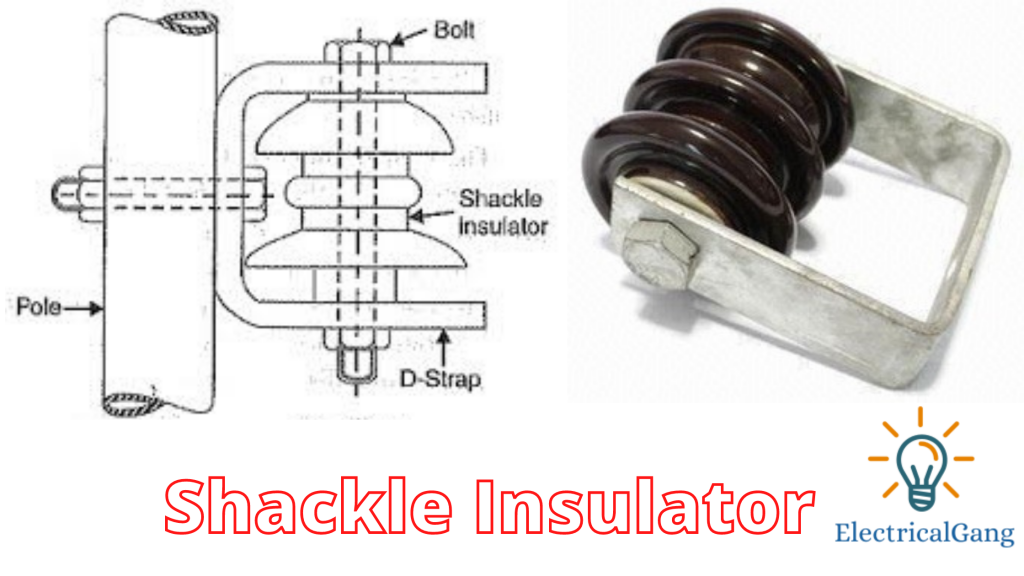
Shackle Insulator is small in size and is used in the overhead distribution line. A metallic strip is used for the attachment of this insulator. The voltage of this insulator is up to 33 kV, and it is used extensively in the line where the turn occurs. We can also use this instead of a strain insulator.
But it is used in low-voltage distribution lines. We can use this in any way while the distribution line is horizontal. Bolts or cross arms are used to attach to the ends of the pole.
Suggested Read: Difference Between Transmission Line And Distribution Line
#3. Post-Insulator:
The post-insulator looks like a pin-type insulator, but it has a lot of mechanical strength. This insulator is overused in the substation as it is perfectly suited for different voltage levels. These insulators are placed in a vertical position which protects transformers, switchgear, and other connecting devices.
This is higher than the pin insulator, which is due to the fact that the number of petticoats is more in the post insulator than in the pin insulator. Porcelain is used in the manufacture of this insulator.
Differences Between Pin Insulator and Post Insulator:
| Sr.no | Pin Insulator | Post-Insulator |
| 1 | This is used up to a 33 kV system. | This is used for both low-voltage and high voltage |
| 2 | It is only available in a single stage. | It is available in both single-stage as well as multiple stags |
| 3 | Cannot fix two insulators simultaneously for high voltage application. | Can fix two insulators or more insulators simultaneously for high voltage application |
| 4 | The conductor is fixed by binding to the top of the insulator | The conductor is fixed to the top of the insulator using a connector clamp |
#4. Suspension Insulator:
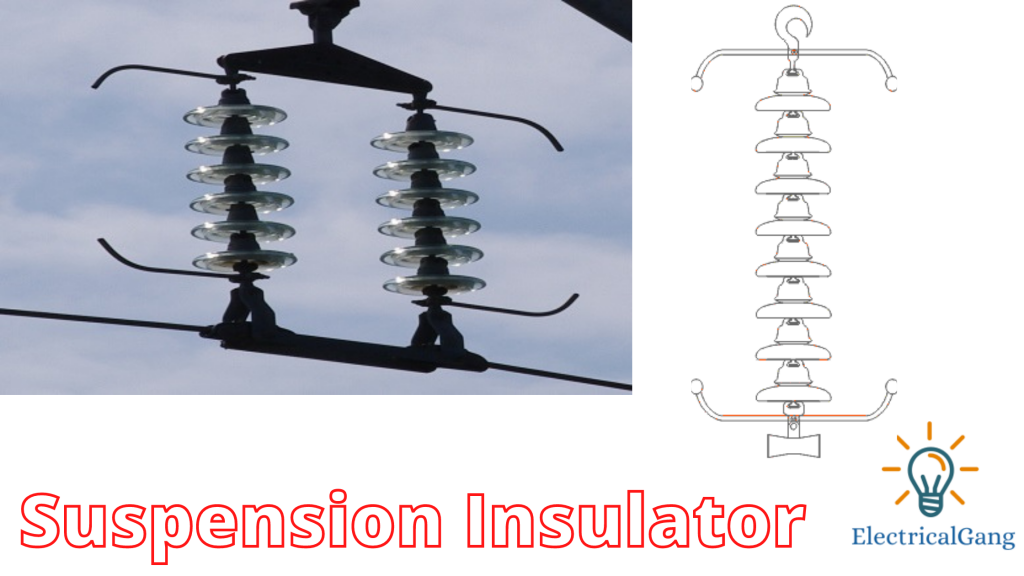
A suspension Insulator is also known as Disc Insulator. Materials such as porcelain or glass are used in the manufacture of these insulators. The voltage capacity of this insulator ranges from 11 kV to 765 kV. As pin-type insulators in more than 33 kV are not suitable for use as they increase in weight and size.
It is only appropriate to use this in an overhead transmission line. Different disks are used depending on the level of voltage. It is attached to the end of the pole so that all the discs get proper support. One of the advantages of this compared to the rest of the insulator is that the rest of the disc works properly, even if one of the discs is damaged. So the damaged disk can be replaced with another.
Suggested Read: Advantages of High Transmission Voltage | Disadvantage of High Transmission Voltage
#5. Strain Insulator:
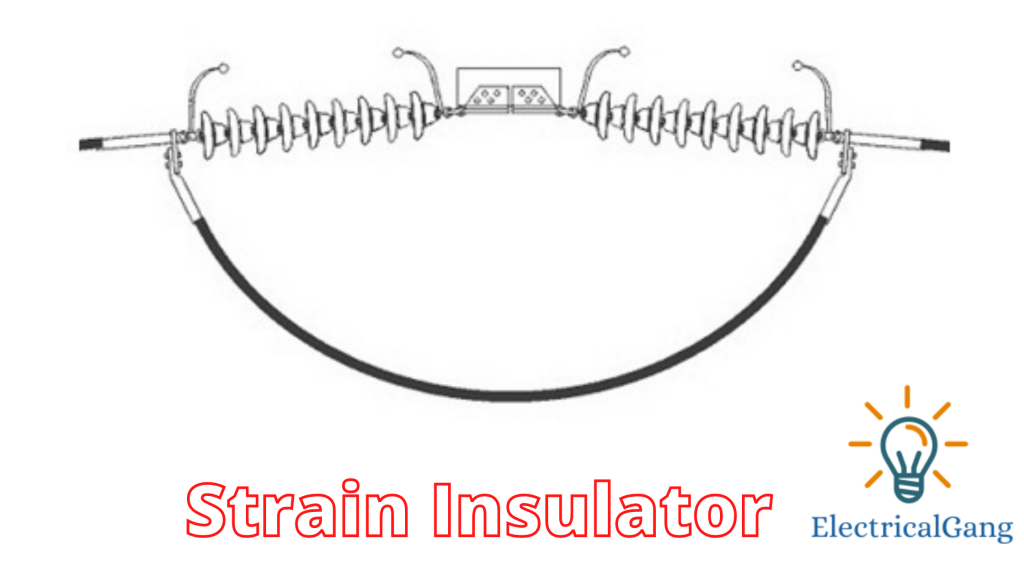
This insulator is very similar in appearance to a suspension-type insulator. This is also used in overhead transmission lines as well as suspension-type insulators. Its function and specifications are different from that. This type of insulator is used when there is a dead-end or where there is a sharp angle in the transmission line.
| Sr.no | Rated System Voltage | Number of Disc insulators used in suspension insulator string | Number of Disc insulators used in strain-type tension insulator string |
| 1 | 33KV | 3 | 3 |
| 2 | 66KV | 4 | 5 |
| 3 | 132KV | 8 | 9 |
| 4 | 220KV | 14 | 15 |
#6. Stay Insulator:
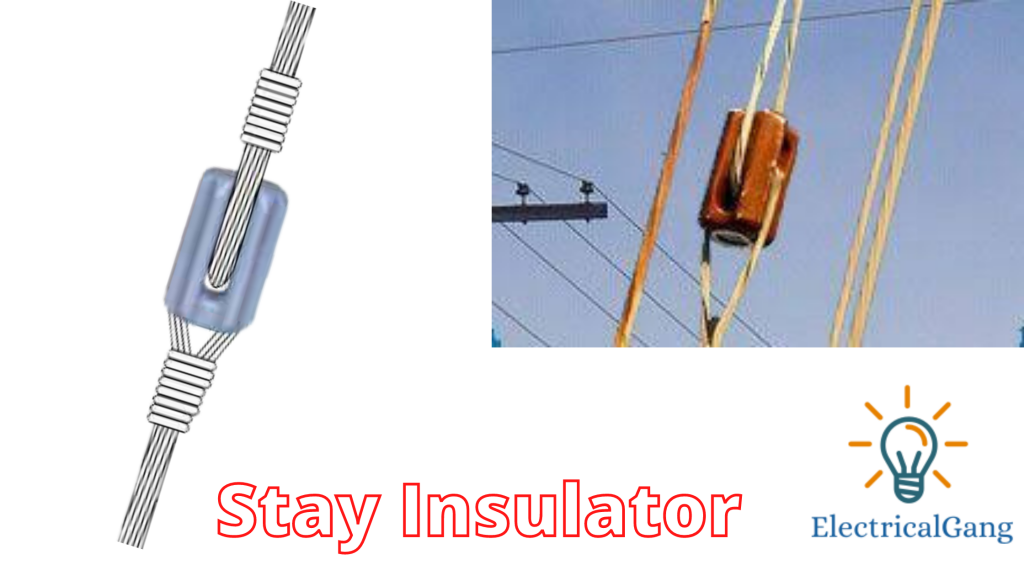

Stay Insulator is rectangular in shape and is used in the distribution lines. While its size is very small compared to other insulators. This is arranged between the line conductor and the earth. This insulator acts like a safety device that protects against sudden defects otherwise, voltage changes occur suddenly.
#7. Disc Insulator:
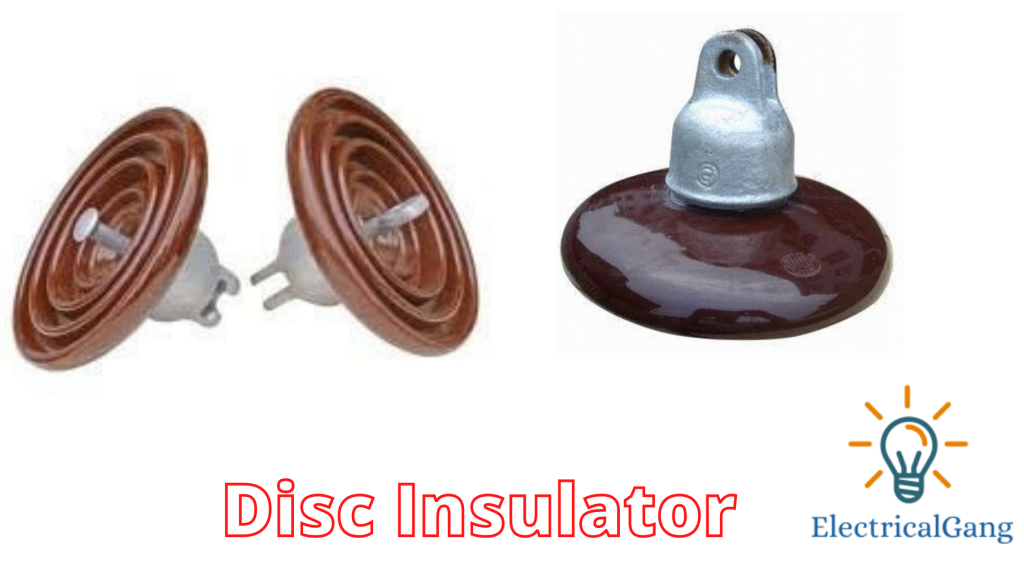

Disc Insulator is made with high-grade raw material. These insulators are properly designed for moderate and low polluted environments at a low cost. These insulators are very popular in the market as they are mostly used in transmission and distribution lines.
These insulators are used in transmission and distribution lines as they have highly efficient features like low corrosion and robust design. It supports conductors used for the insulation of cables and electrical wiring.
Other Types of Electrical Insulators:
Other types of insulators include the following insulators.
| Sr. No. | Other Types of Electrical Insulators |
| #1. | Polymer Insulator |
| #2. | Glass Insulator |
| #3. | Long Rod Insulator |
#1. Polymer Insulator:
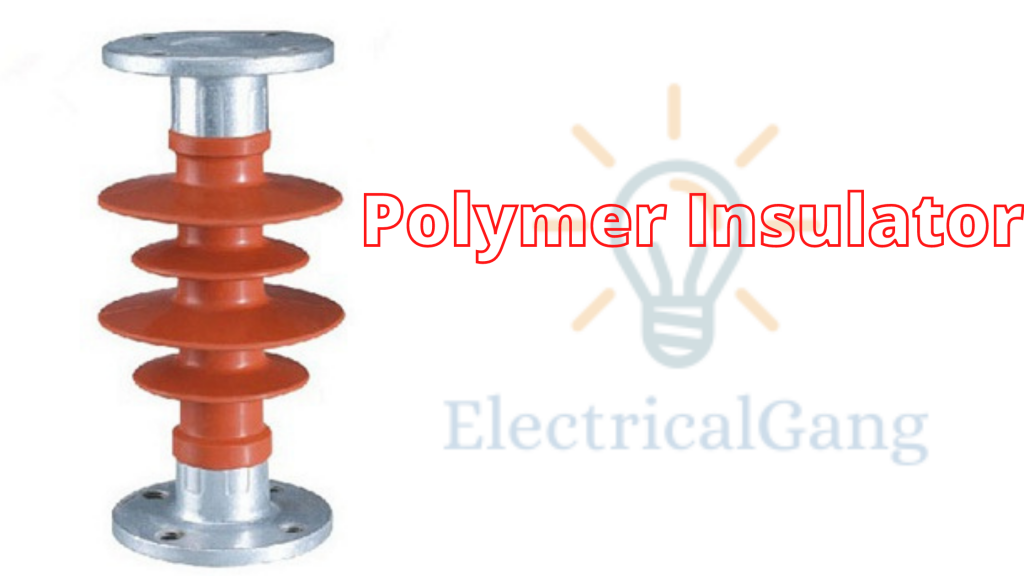
Polymer Insulator is made with silicone rubber, PTFE, EPDM, and EPM. It weighs less than porcelain-type insulators. These insulators are made of fiberglass rods and bonded with a polymer weather shade.
#2. Glass Insulator:
Glass Insulator was used in the 18th century for telegraph and telephone lines. Which were replaced in the 19th century with ceramic and porcelain types. The reason for the prevalence of this insulator was longevity.
#3. Long Rod Insulator:
In this insulator, the units do not contain any metal parts, which helps to increase their strength. These are just porcelain rods that include weather sheds and outside metal end fittings. Both stress and suspension apply in places.
Applications of Electrical Insulators:
The use of electrical insulators is as follows:
- This insulator protects the material from lightning and heat.
- In terms of safety, it is used in circuits and electric boards.
- Plastics and rubbers are used for the production of everyday products.
Type of Insulator in Transmission Line:
| Insulator Type | Voltage capacity | Use |
| Pin insulator | < 33 kV | Distribution system |
| Post insulator | 11 kV to 765 kV | Substation system |
| Shackle insulator | < 33 kV | Distribution system |
| Suspension insulator | > 11 kV (High) | Transmission system |
Types of Insulators in Transmission Lines:
| Insulator Type | Voltage capacity | Use |
| Pin insulator | < 33 kV | Distribution system |
| Post insulator | 11 kV to 765 kV | Substation system |
| Shackle insulator | < 33 kV | Distribution system |
| Suspension insulator | > 11 kV (High) | Transmission system |
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

What are the types of insulators?
Insulators are classified based on their rating and are mainly used for transmission lines. The types of insulators are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Insulator Types |
| #1. | Pin Insulator |
| #2. | Shackle Insulator |
| #3. | Post-Insulator |
| #4. | Suspension Insulator |
| #5. | Strain Insulator |
| #6. | Stay Insulator |
| #7. | Disc Insulator |
How many types of electrical insulators are there?
The insulators used as overhead insulators in the transmission line are as follows:
- Pin insulator.
- Suspension insulator.
- Strain insulator.
- Shackle Insulator.
What are common electrical insulators?
The most effective insulators to provide a barrier between conductors to control the electric current are shown below.
- Rubber.
- Glass.
- Pure water.
- Dry wood.
- Dry cotton.
- Oil.
- Air.
- Diamond.
What are 4 examples of insulators?
Examples of insulators include plastics, Styrofoam, paper, rubber, glass, and dry air.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –