As we know, there are many types of motors available in the market. The function of each motor depends on its need. In normal life, one must use a human motor in some way that can increase the performance of the motor. Not every motor uses the same type of equipment, but it depends on its type and requirement.
The optimization of the stator can be improved by the rotor as well as the optimization methods to improve the performance of the motor. In motors and in electrical machines such as generators, the stator plays an important role. In today’s article, we will see what is a stator, what is its working principle, why is a stator constructed, etc.
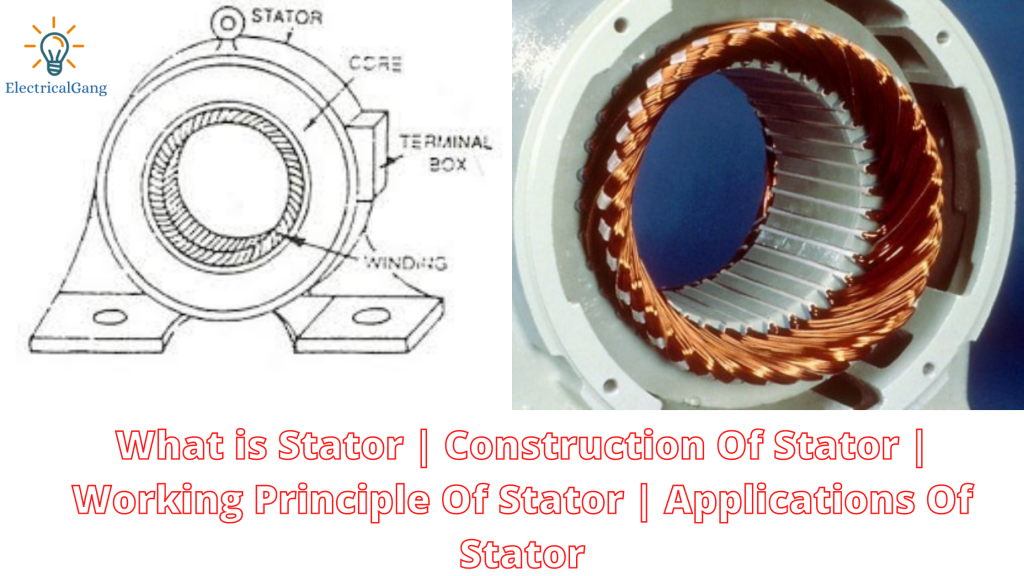
What is Stator?
The stationary part in a motor is called a stator, while the rotating part is called a rotor. There are many windings inside the stator. Its polarity is constantly changing when AC power is given to it. When this gets power, an alternating current is provided in the winding to create an electromagnetic field towards the bar in the rotor.
So this will rotate the magnetic field due to AC power. It has thin and stacked laminations that are wound with the help of an insulated wire. This includes the number of stacked laminations in the core.
Suggested Read: What Is an Induction Motor | Types of Induction Motor
The diagram of the stator is as follows:

The motor can be designed up to a maximum of 22 kW, while motors with high output have cast-iron housings. The main function of a motor is to handle the voltage, output, different frequencies, and unstable poles.
Construction of Stator:
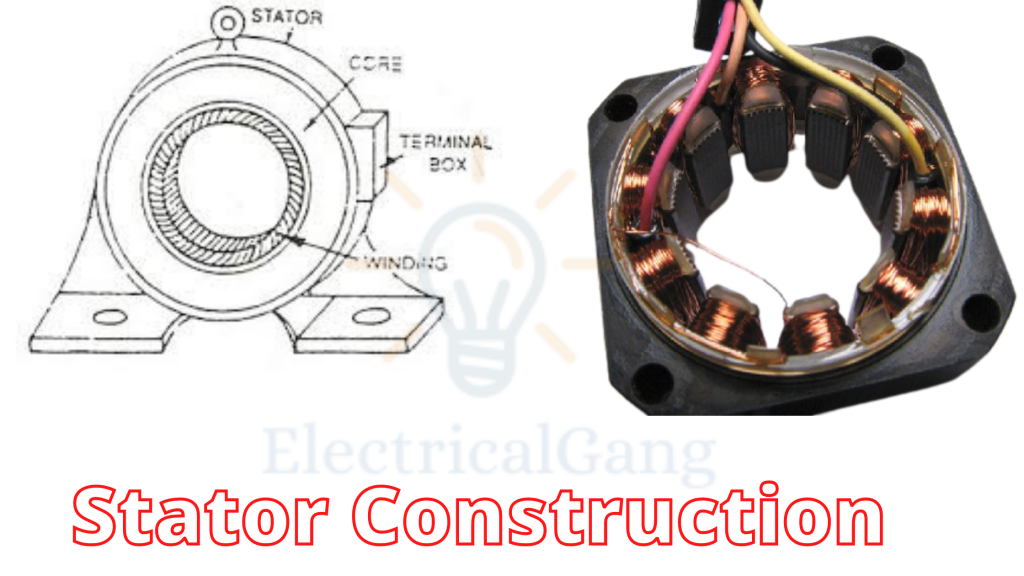
This is designed with high-position alloy steel laminations to reduce the loss of the eddy current of the motor.
The motor consists of three main parts, which are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Motor Consists of Three Main Parts |
| #1 | Outer frame |
| #2 | Core |
| #3 | Windings |
#1. Outer frame:
This part can be known by its name which is the outer part of the motor. Its main function is to support the core of the motor and the inner part.
#2. Core:
The core is made of silicon steel stampings. Its main function is to capture an unbalanced magnetic field to produce an eddy current and hysteresis damage. The core of the motor is attached to the frame in which the stator stamping is insulated with the help of varnish. Varnishing changes the thickness of the stepping from 0.3 mm – 0.5 mm; attachments of slots can occur in stamping.
Suggested Read: What Is a Solenoid Coil | Working Principle of Solenoid Coil
#3. Windings:
3 phase winding is done in the main part of the stator through which this motor gets power. Three sets of these windings are used so that we get 6 ends on the outside. Inside the motor, this winding is set precisely depending on the speed of the motor.
If the number of poles in the motor increases, then the speed of the motor decreases, but if the number of poles decreases, then the speed of the motor increases. The winding connection in the motor is made in delta or star.
The relationship between motor and speed can be given on the basis of the following formula.
Ns ∝ 1/p otherwise Ns = 120f/p
Working Principle of Stator:
When power is supplied to this motor, a rotary magnetic field is generated in it. Its function varies depending on the machines, such as motors, generators, and fluid-operated devices. The rotary generates a magnetic field to drive the rotor in the motor.
A generator converts a rotary magnetic field into an electric current. Similarly, fluid-operated devices direct the flow of fluid in the direction of the moving part of the system.
Applications of Stator:
The use of stator is as follows:
- Provides a rotating magnetic field to the rotor/armature rotating in the motor.
- The rotating electromotive acts as a field magnet in the motor based on the design.
- A generator converts from a rotating magnetic field into an electric current.
- In fluid-operated equipment, it shows the path of fluid flow in the rotary part of the system.
Stator Construction:
The frame of the stator consists of a lamination of silicon steel. It is usually about 0.5 millimeters thick. Lamination is necessary because voltages are induced in the axial length of the steel as well as in the stator conductors. The laminations are usually insulated from each other by a varnish layer.
Suggested Read: What Is a Motor Starter? | Types of Motor Starters
Stator Working Principle:
In an electric motor, the stator works to provide the magnetic field, which drives the rotating armature. In a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field into electrical energy. In fluid-driven devices, the stator guides fluid flow to or from the rotating part of the system.
What Is the Primary Function of Stator Core?
In an electric motor, the stator works to provide the magnetic field, which drives the rotating armature. In a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field into electrical energy. In fluid-driven devices, the stator guides fluid flow to or from the rotating part of the system.
Stator Working:
The working principle of the stator is that it will generate a rotary magnetic field due to the 3 phase power supply. Its function varies depending on the motor, generator, and fluid-driven device. In a motor, it provides a rotary magnetic field to drive the rotary armature.
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

How Is a Stator Constructed?
The stator core is made of a thin punched lamination of electrical grade steel. What we commonly call “punches.” They are split, which means that 12 to 24 punches are laid side by side to form a complete 360° ring with a single layer.
What are the parts of the stator?
The essential parts of the stator are the outer frame, core, and winding.
What Is the Principle of Stator?
When power is supplied to this motor, a rotary magnetic field is generated in it. Its function varies depending on the machines, such as motors, generators, and fluid-operated devices. The rotary generates a magnetic field to drive the rotor in the motor.
What Is the Construction of 3 Phase Induction Motor?
The stator is a stationary part of the motor. The winding is placed in the stator, and it is supplied with a three-phase supply. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor.
Where Is DOL Starter Used?
The DOL starter is mainly used to start the motor. Where high inrush current does not cause an excessive voltage drop in the supply circuit. The direct online starter is mainly used to start a small water pump conveyor belt, fan, and compressor.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –