The Buchholz relay was first used by Max Buchholz in 1921. Relays are used for security purposes. Which we use for power transmission and distribution.
This relay is mounted on the top of the transformer. Which is used as a protective cover for the dielectric failure of the transformer. As current leakage, fractional discharge, hot spots, and arcing are events that act as oil corrosion insulation by producing a dangerous flow. The transformer produces a dangerous flow of gas in the tank.
When the transformer was closed, it has a big economic impact on the power supply network operation. Thus, it aims to ensure accurate measurement of the position of the transformer. In today’s article, we will see what is Buchholz relay, what is its construction, what is the working principle of Buchholz’s relay is, and what are its uses.
What is Buchholz Relay?
Buchholz Relay is used for the protection of the transformer. Used for transformers larger than 500KVA and filled with oil. The Buchholz Relay is a relay that reacts with oil and gas.
This is used to protect the transformer from all these defects such as short circuit, inter-turn, core, insert, etc. inside the transformer. The relay will understand all these defects and it will be turned off with the help of the alarm circuit.
Suggested Read: What Is a Coupling Capacitor | Construction of Coupling Capacitor | Applications of Coupling Capacitor
Construction of Buchholz Relay:
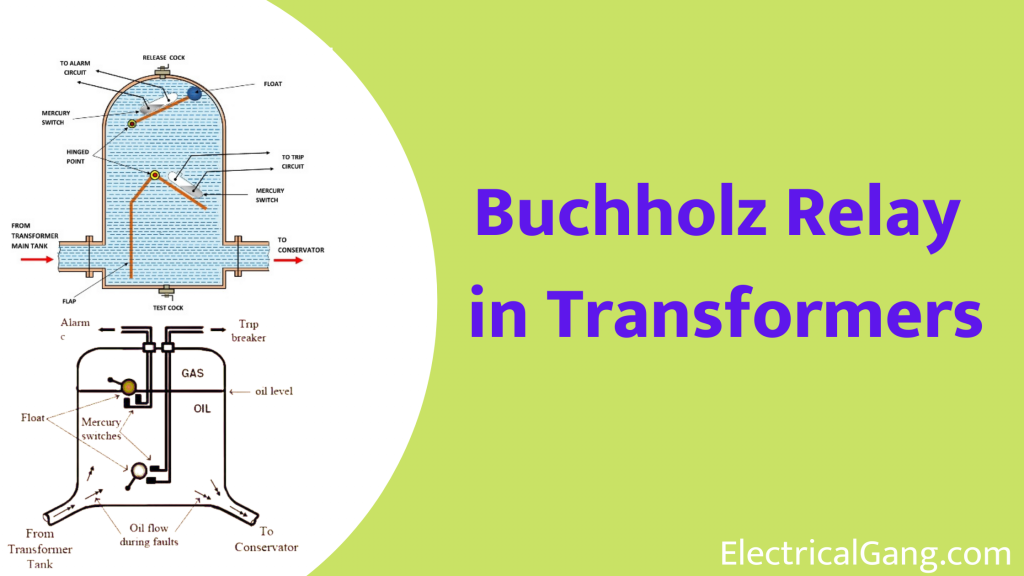
Inside the Buchholz Relay is an oil tank. It has two hinged floats. A mercury switch is attached to both of these floats in the top part of one tank and in the bottom part of the other tank. The upper float mercury switch is connected to the alarm circuit. While the bottom float switch is connected to an external trip breaker. The figure below is for further understanding.

Working Principle Buchholz Relay:
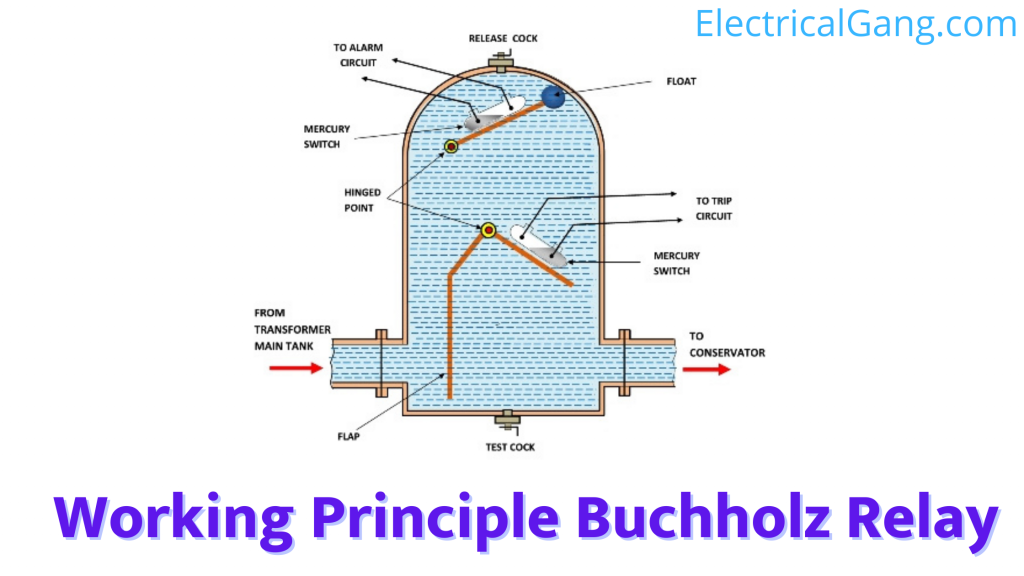
The principle of working with Buchholz Relay is very easy to understand. This relay is capable of working mechanically. This means being mechanically active at work. When there is a small defect inside the transformer such as its insulation failure, the increase in temperature will stop the transformer from working.
Different hydrocarbons will decompose into gases, such as CO2 and CO. Until the transformer insulating oil dissolves, Buchols will accumulate at the top of the container, causing the oil level in it to drop. Lowering the oil level means lowering the float position and tilting the mercury switch. The contact of this mercury switch is closed and the alarm circuit is activated.
Sometimes bubbles of air can accumulate in the upper part of the Buchholz container due to leakage in the main tank of the transformer. This will also lower the oil level in the tank and activate the alarm circuit. By collecting and analyzing the gas from the gas release point at the apex of the relay, we can know that we can predict the faults of the transformer.
Extremely serious faults such as a short circuit occurring between the phase and the earth are the faults in the tap shifting equipment which brings a surge in the oil and which strikes the baffle plate. And causes the lower-level mercury switch to shut down.
The circuit connected to the transformer from the switch stimulates the trip circuit of the breaker and separates the faulty transformer from the rest of the electrical power system of the inter-tripping connected to both sides of the LV and HV connected to this transformer. This is how the Buchols relay works.
How Does A Buchholz Relay Work?
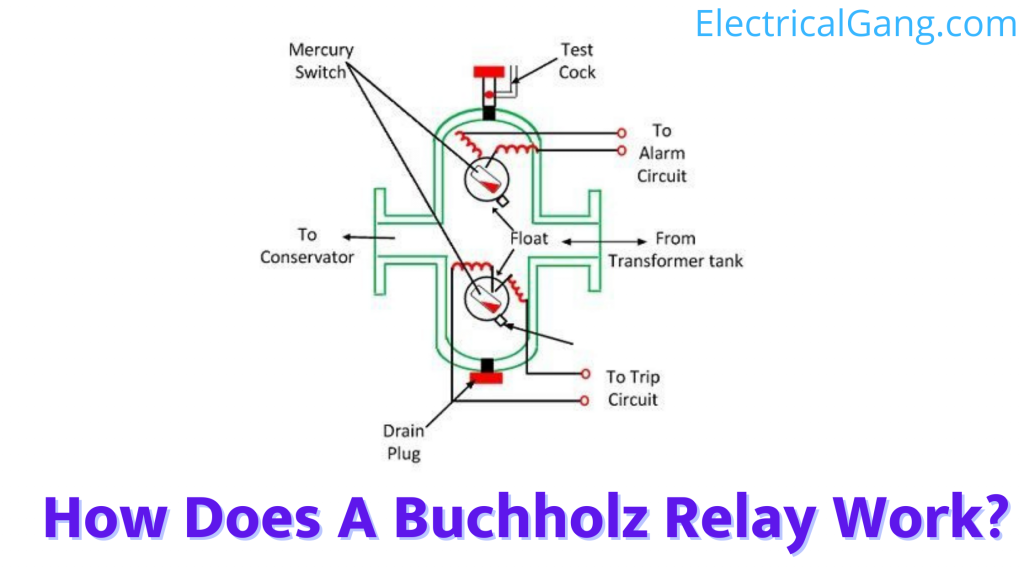
Whenever there is a major or minor defect in the transformer, heat is emitted by the defect. And this heat is the main cause of the decomposition of oil. So that gas bubbles are created and continue to flow upwards which gathers the Buchholz Relay.
The collected gas transfers the oil and hence the displacement is equal to the proportion of the collected gas. Due to the transfer of oil, the upper mercury switches off due to the above float. Which is connected to the alarm switch. So this alarm is activated even if any small problem has occurred. The amount of gas stored indicates the severity of the defect that occurs.
The small problem is not enough to move the bottom float so the bottom float does not affect it. If there is a major defect like a phase-to-earth short circuit then a large amount of gas is produced in such a problem. This gas will go up just like a small fault but this gas is enough to bend the bottom float. In this case, the lower float can source a low mercury switch that can travel from the supply to the transformer.
Buchholz Relay Testing Procedures:
The methods for testing Buchholz Relay are as follows:
- Leakage Test.
- Electrical Test.
- Functional Test.
#1. Leakage Test:
- The Buchholz Relay can be packed with oil at a temperature of 90° C and the force of the bar and can be checked for outflow after 30 minutes.
#2. Electrical Test:
- The connections of the earthing insulation are ensured by running a 2000 V voltage for 1 minute.
#3. Functional Test:
- Buchholz Relay is tested by a PLC panel specially designed for this purpose. Also, the response status of all the contact systems will be checked.
Advantages of Buchholz Relay:
The Benefits of Buchholz Relay Are as Follows:
- The severity of the defect can be determined without opening the transformer.
- The Buchholz Relay heat shows the internal cause which helps to avoid its major defects.
- The transformer can be easily disassembled with the help of this relay to prevent accidents if any major defects occur.
Disadvantages of Buchholz Relay:
The disadvantages of Buchholz Relay are as follows:
- This only works for oil-absorbing transformers.
- This relay can detect faults only when the oil level is low
- Separate protection is required for the cable as it does not protect the cable attached to the transformer.
- High reaction time.
- The shortest operating time of this relay is 0.1 seconds.
Applications of Buchholz Relay:
The application of Buchholz Relay is as follows:
- Insulation failure of core bolts.
- Bushing Pierce.
- Short circuit between stages.
- Winding short circuit.
- This relay can be used in loose and bad electrical contacts.
Operating Conditions of Buchholz Relay:
The Buchholz Relay operates in three main scenarios as follows:
- When any small or big mistake due to bubbles forming in it.
- Whenever oil leaks from the transformer and its level decrease.
- Whenever oil in the transformer flows from the protection tank to the main or from the main tank to the protection tank.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –