The main function of the heat sensor circuit is to sense heat, which is located on this side of the sensor. When the temperature exceeds a certain value, it is displayed with the help of a flashing LED. Heat sensor circuits are used in various places, such as in all our computers and in large high-tech kitchens, etc.
Excessive heat can damage a computer or equipment in a high-tech kitchen. It senses this heat when the temperature around the heat sensor exceeds its specified temperature. Gives a hint. So that we can keep our devices safe. Using heat sensors, we sense heat from various electronic devices such as amplifiers, computers, etc., and thus generate warning alarms.
Operating Principle of Heat Sensor Circuit Diagram:
A simple diagram of the heat sensor is shown below. The BC548 transistor thermistor (110 ohms) is one of the few components used in heat sensors. A clear explanation of these components is given below.
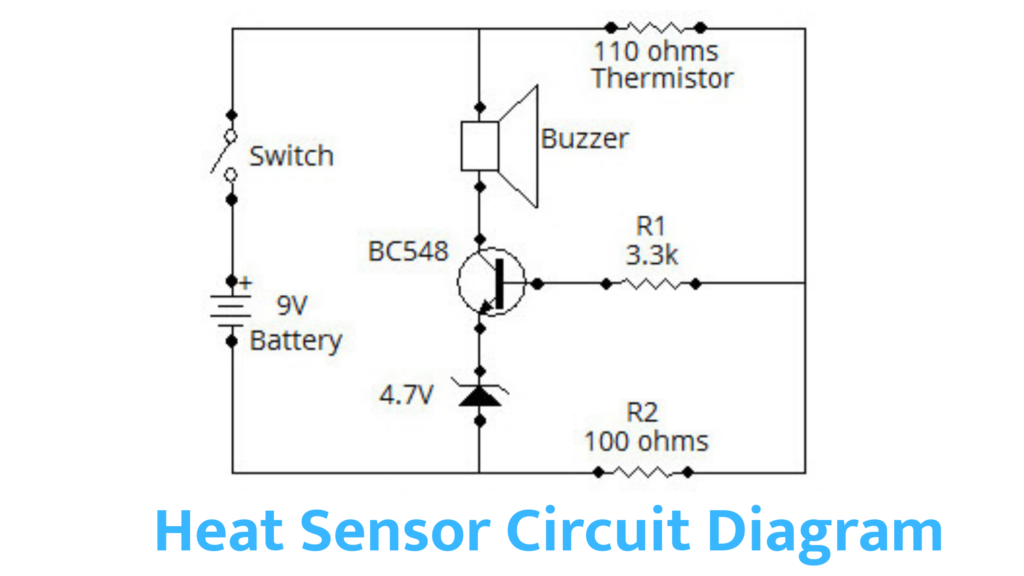
110 Ohms Thermistor: This thermistor is used to detect heat.
Buzzer: Buzzer is between the + 9V battery and the collector terminal of the transistor. The alarm sounds when the temperature rises above the set value.
Zener Diode: 4.7 V Zener Diode is used to control the emitter current.
BC548: BC548 is an NPN-type transistor. This transistor can be replaced by other transistors like 2N2222, BC168, BC238, and BC183, as the characteristics of the transistor shown above are almost the same.
R1, R2: 100 ohms 1/4 d is used as R2, and 3.3 or 1/4 d resistor is used as R1.
9V Battery: This battery is used to power the circuit.
Switch: In this circuit SPST switch (Single Pole Single Throw) is used. It is your choice to use this switch is not mandatory.
In the above circuit, 100 ohms, resistors, and thermistors are connected in series. If the thermistor is of negative temperature coefficient type, then its resistance decreases after heating the thermistor. And more current flows through the thermistor. This results in a higher voltage across the resistance junction and the thermister.
It is applied to the NPN transistor by the voltage resistance of the output. The emitter voltage is maintained at 4.7 V by a Zenor diode. This voltage is used as a comparable voltage. If the base voltage is greater than the emitter voltage, the transistor carries it. If the transistor receives more than 4.7 V base voltage, it operates and completes the circuit through a buzzer and produces noise.
Heat Detector:
A heat detector is a fire alarm system device that detects fire or heat in the atmosphere. Changes in heat that exceed the limits of the heat sensor are detected by the heat sensor. To avoid a serious accident such as a fire, the heat sensor produces a signal that gives instructions and helps prevent fire damage.
Suggested Read: Different Types of Sensors Used in Automobiles
Heat Detector Circuit:
The heat sensor is used with Heat Detector Circuit. It is designed to represent changes in fire and temperature. It is used as a fire warning. It is classified into two sections based on its operation, which are as follows.
- Fixed Temperature Heat Detectors.
- The Rate of Rising Heat Detectors.
#1. Fixed Temperature Heat Detectors:

This heat detector uses two heat-sensitive thermocouples. One thermocouple reacts to the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere, while the other thermocouple is used to monitor heat, which is transferred by radiation or convection. The heat detector operates regardless of the starting temperature. The temperature rises from 12˚ to 15˚F per minute. This detector can also be operated with low-temperature fire conditions if the type of heat detector threshold value is determined.
#2. The Rate of Rising Heat Detectors:

This does not respond to low energy light rates that deliberately develop a fire. This compound detector adds a fixed temperature element that is used to detect slowly developing fires. This element reacts whenever a fixed temperature element reaches the threshold. Usually electrically connected fixed temperature point 136.4˚F or 58˚C.
Temperature Sensor:
It senses the heat generated by any system or thing, which allows us to detect or detect any physical change due to the temperature generated by an analog or digital output. Depending on the application, temperature sensors are classified into different types with different characteristics. There are two basic types of temperature sensors.
Contact Temperature Sensor Types–These types of sensors are widely used to detect liquids, solids, or gases. The temperature sensor needs to be physically in contact with the object. And it uses conduction to monitor changes in temperature.
Non-contact Temperature Sensor Types–This type of sensor uses temperature sensor radiation and convection to monitor changes in temperature. These types of sensors are used to detect gates and liquids that emit radiant energy, which is transmitted in the form of infrared radiation.
Suggested Read: Components of Operating System | A Comprehensive Guide
Temperature Sensor Circuit:
The temperature sensor circuit diagram is shown below. LM 35 is used as a temperature sensor in this circuit. The main function of this sensor is to detect a certain centigrade temperature.
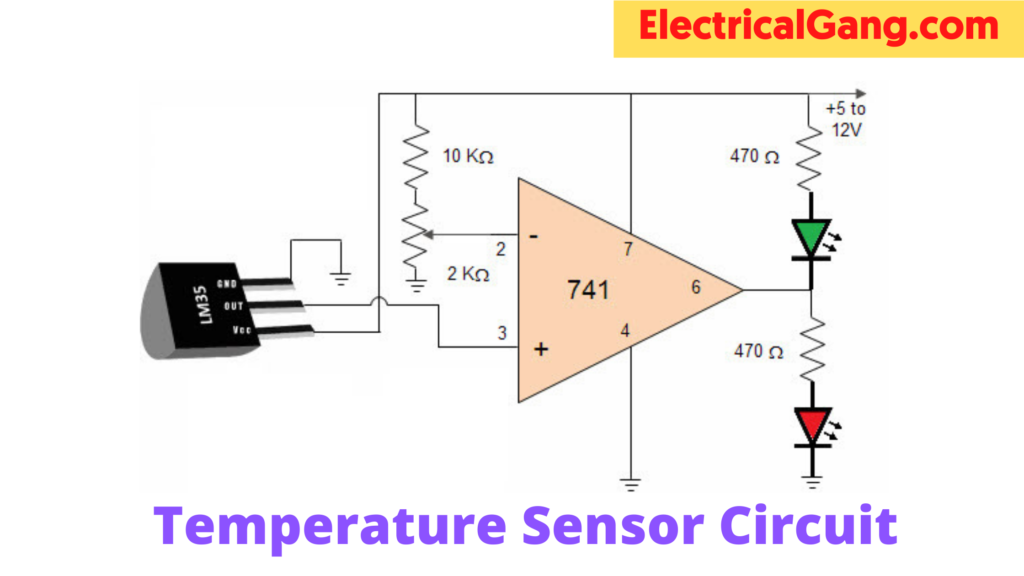
The linearity of the IC sensor with the opposite accuracy from the thermister has very good accuracy at 0.5°C and a sufficient range of temperature. Its output is comparable to Celsius temperature. The IC temperature operating range is -55° C to + 150° C.
It draws just over 50 µA from its supply, and the main characteristics are self-heating and <0.1 degrees centigrade in air. The IC operating voltage ranges from 4 volts to 30 volts, and the output is 10mv°C. In this circuit, the voltage can be set to IC pin 2 using a potentiometer. The circuit can be designed to activate or deactivate the device at specific edge temperatures. Temperature can be indicated using two LEDs called green LEDs
If the output temperature of the secondary exceeds ten mV, then this changing voltage is the supply of the IC 741 OP amplifier. This is mostly used in integrated circuits. It has two terminals. Such as inverting (input (-)), and non-inverting (output (+)). The 741 op-amps are used as an amplifier in this circuit. This means that the input pin is pin-3, and the Output pin is in. This circuit widens the gap between its input terminals.
Advantages of Temperature Sensor:
The advantages of temperature sensors are as follows:
- It does not have any effect on the medium.
- Replies immediately.
- It has an easily conditioned output.
- Its accuracy is high.
Suggested Read: What is a Motion Sensor? | Types of Motion Sensor
Heat Detector Tester:
The different types of Heat Detector Tester are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Different Types of Heat Detector Testers |
| #1. | Smoke Detector Test Equipment |
| #2. | Solo 330 Smoke Dispensers |
| #3. | Solo 461 Cordless Heat Tester |
#1. Smoke Detector Test Equipment:
This detector uses smoke test aerosol and solo aerosol. This ensures that the detector will not leave any residue and will not be filled with particles. A simple shot blast is enough to set the detector to make an alarm sound. Using the Solo 200 Removal Tool, the detectors can be removed and operated.
#2. Solo 330 Smoke Dispensers:
Solo 330 Smoke Dispensers are light in weight and easy to use, and strong. The Solo 330 is primarily made for the purpose of increasing use with the Solo Aerosol. The swing frame and injection molded construction make it an ideal tool for testing. The Solo 330 has features.
- Touch-sensitive.
- Strong.
- Spring-filled mechanism.
- High strength and durability.
#3. Solo 461 Cordless Heat Tester:
The infrared beam is broken with the help of this detector to activate heat generation. Direct is directed into the sensor of the detector. For added security, it shuts off after 5 minutes.
Heat Sensor Working Principle:
A temperature sensor works by providing a reading through an electrical signal. The sensor is mainly made of two metals, which produce an electrical voltage or resistance when the temperature changes by measuring the voltage across the diode terminals. When the voltage increases, the temperature also increases.
Circuit Temperature Sensor:
Temperature sensor circuit:
An IC Temperature Sensor is a two-terminal integrated circuit temperature transducer that produces an output current proportional to absolute temperature. The sensor package is small, with a low thermal mass and a fast response time. The most common temperature range is 55 to 150°C (-58 to 302°F).
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

What Is Heat Sensor Circuit?
A heat sensor circuit typically includes a heat sensing component thermistor, which works similarly to a resistor and changes its resistance upon sensing heat, a variable resistor, a transistor, a buzzer for alarming, and a capacitor. This circuit can be used for various purposes.
How Do You Make a Temperature Sensor Circuit?
The components you need to make a temperature sensor are a 9V input DC supply DC, a 10KΩ thermistor, a BC547B transistor, a 6V relay, a 1N4007 diode, and a 20KΩ variable resistor. This circuit can be operated with a 9V battery, adapter, or transformer.
What Are the 2 Types of Temperature Sensors?
There are currently four types of temperature sensors in the market, which are most widely used in electronics nowadays, which is something like this. Thermocouples, RTDs (resistance temperature detectors), thermistors, and semiconductor-based integrated circuits (IC).
Where Are Heat Sensors Used?
This circuit is used in many electrical devices in all of our homes, such as refrigerators and freezers, to help control and maintain cold temperatures, as well as to ensure that stoves and ovens are heated to levels required for cooking and air confectioners/heaters.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –