Induction motors rotor lock currents and starting currents look alike but are not in fact different. The word is also different and the meaning is also different. So friends, in today’s article we will see what is the difference between Locked Rotor Current and Starting Current.
Locked rotor current is mainly taken by the motor when the rotor of the motor is to be kept in a stationary position. This means that the rotor of the motor does not make any movement. This means that whenever we start any motor, its rotor is in a resting position. This means that the on and off rotor start must be the same. Isn’t it No, it’s not. How?
We all know that the motor is turned on in different ways. If we use one of these systems’ direct online starter then the voltage coming to the terminal will be the rated voltage of the motor. In any motor, there is a rest before the movement of the rotor starts. And voltage is considered voltage.
Suggested Read: What Is a Motor Starter? | Types of Motor Starters | Advantage of Motor Starter
The current given at the beginning is equal to the rotor current. Instead of this, if any other motor is used to start, such as Star Delta or Soft Starter, the motor is started at low voltage. Therefore the current will be less than the current lock rotor current.
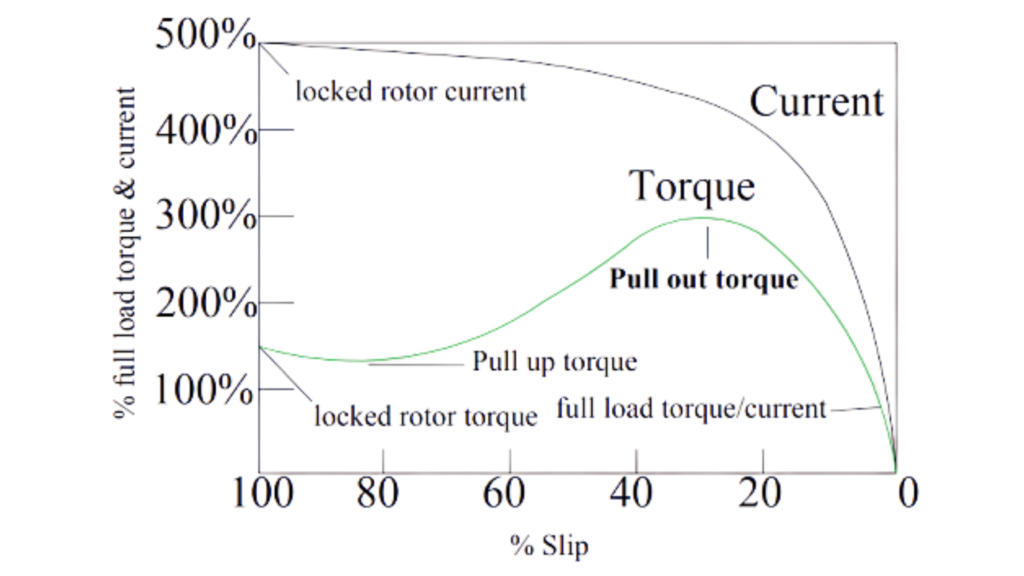
The big and important difference between these is that there may be a closed rotor at any time during the operation of the motor. For example, let us consider the motor running normally under its rated load. Taking a load suddenly higher than its own rating will increase its speed and consequently increase the torque of the motor.
Suggested Read: What is Electric Motor? | Different Types of Electric Motors
But if the load torque requirement is more than the motor torque then the motor will take more current and produce enough torque as required and go to the maximum limit. But if the load torque requirement is more than the pull-out torque then the motor speed will be zero. This is the case of a closed rotor. There could be many reasons for this. In which single-phase power, bearing jamming, load jamming, etc.
In this way, the rotor current is taken until the rotor is stopped or stopped, while the starting current is taken while starting the motor.
Locked rotor current should not stay for a long time otherwise insulation may also fail due to overheating problems. Or the stator or rotor is likely to burn out.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –