Hello friends, in today’s article we will talk about what is tube light, what components are used, and what is its working principle.
What Is Tubelight?
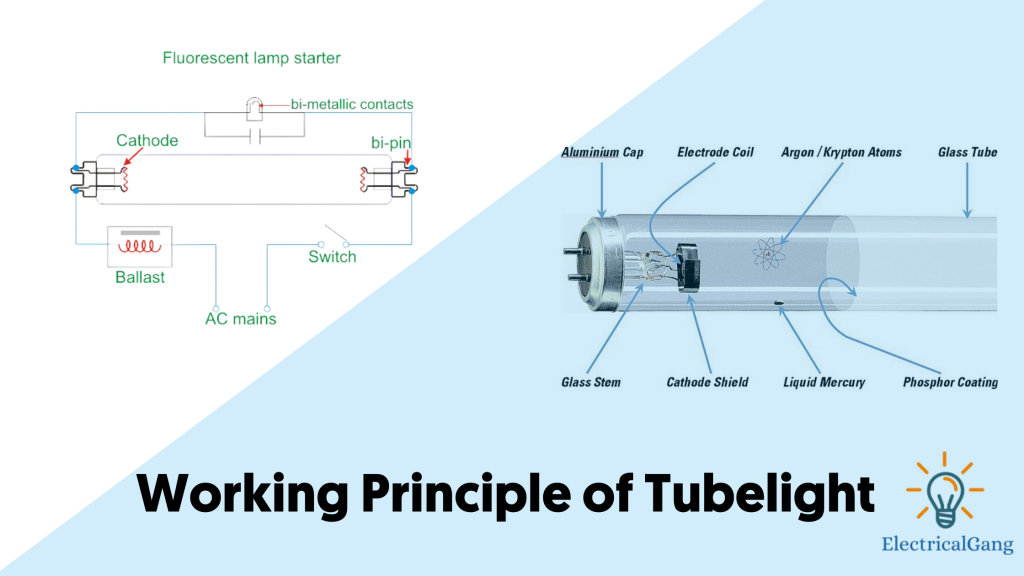
A fluorescent lamp with a cylindrical tube is known as a tube light. Tube light is a type of lamp that works on the dissolution of low-pressure mercury vapor, which converts ultraviolet rays into visible rays using a phosphor-coated inside a glass tube.
Material Used Inside the Tubelight

The materials used mainly inside the tube light are as follows
- Endcap.
- Glass stem.
- Mercury drop.
- Inert gases (argon).
- Electrode shield.
- Filament coils as electrodes.
- Phosphor-coated glass bulb.
Suggested Read: What Is a Motor Starter? | Types of Motor Starters | Advantage of Motor Starter
Auxiliary Electrical Components Along with Tubelight

When the tube light is given 220 volts of power, it does not work directly. In such a situation, it needs an auxiliary component.
Which consists of 2 components Ballast and Starter:
- Ballast: It can be electromagnetic ballast or electronic ballast.
- Starter: A small neon lamp is used inside the starter, which includes a fixed contact bimetallic strip and a small capacitor.
Working Principle of Tubelight
When we power the tube light the whole voltage will go to the electronic ballast and to the starter of the tube light then it comes to the tube light side so, in the beginning, we will not get any kind of light from it. The first voltage goes into the starter as the distance between the electrodes in the starter’s neon bulb is much less than in a fluorescent lamp.
Due to the given voltage, the gas inside the starter becomes ionized and heats the bimetallic strip. Which is caused by being bent to engage in fixed contact. Now the current continues to flow from the starter, although the probability of ionization of neon is slightly higher than that of argon. This is due to a small electrode gap.
As the voltage decreases due to the current as the voltage drops in the inductor the strip cools and moves away from the fixed contact at the moment a large L di / dt voltage surges across the inductor at break time. This high-value increase occurs on the tube light electrodes and strikes the panning mixture (a mixture of argon gas and mercury vapor).
The process of gas discharge continues and currently, the tube light gets its way to flow through the gas only because of the lower resistance than the resistance of the starter. The secretion of mercury molecules produces ultraviolet radiation which in turn stimulates the phosphor powder coating to radiate visible light. In the operation of the tube light, the starter becomes inactive.
Suggested Read: Highway/Street Light Names And Functions
Required Wiring Components
Although the tube light is not directly connected to the incoming current in our home or office, it operates at 230 V, 50 Hz. There are total electrical components for single tube light installation.
- Starter: Small neon glow up the lamp.
- Switch.
- Wire.
- Choke: It is an electromagnetic ballast or electronic ballast.
Wiring Diagram of Single Tube Light Installation with Electromagnetic Ballast
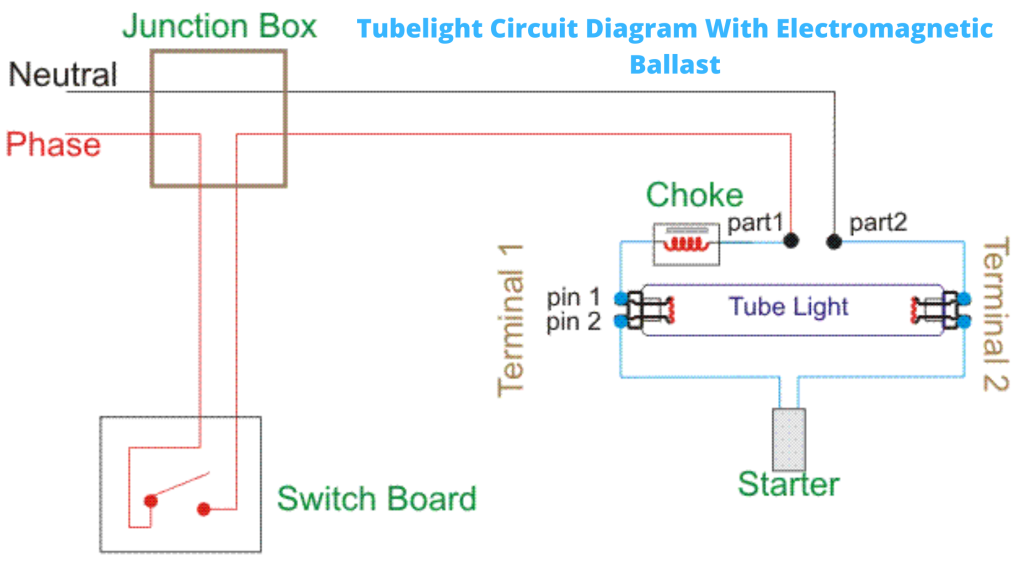
How to Install a Single Tube Light with Electromagnetic Ballast?
The neutral wire from the main junction box is not carried to the switchboard it is connected to Part 2 of the direct tube light.
This neutral wire is already connected to pin 1 of the terminal of the tube light with the help of a wire so the connection of this wire runs from part 2 to pin 1 of terminal 2 without any obstruction. live wire i.e. main phase is given in part 1 by breaking with the help of a switch.
It is fed into the ballast with the help of a wire from part 1. The second nickel of the ballast is given to the end in pin 1 of terminal 1.
Now both ends of the leftover starter are connected one by one to pin 2 of terminal 1 and the other end is connected to pin 2 of terminal 2.
Suggested Read: Buchholz Relay in Transformers | The Definitive Guide
How Tubelight Works?
A fluorescent lamp produces light by the collision of free accelerated electrons with atoms in hot gas. Usually mercury – in which electrons are bumped up to higher energy levels and then fall back while emitting two UV emission lines.
Frequently Asked Questions

How does a Tubelight starter work?
When we turn on the tube light the starter is off. The filaments on both ends of the tube are heated by electricity. This creates a cloud of electrons inside the tube. When it opens, the voltage towards the tube can allow the flow of electrons to flow through the tube and ionize the mercury vapor.
What is the working of the choke in the tube light?
The purpose of the square is to provide a very high voltage at the beginning of the filaments (towards both ends of the tube light). Once again the choke provides low voltage after the gas is ionized in the tube.
How tube light circuit is connected and how it work?
When we give the power to turn on the tube light, the voltage comes to this side with the help of the starter and ballast and due to full voltage, the gas in the starter becomes ionized and heats the bent bimetallic strip to be connected to a fixed contact.
How do I know if my tube light is working?
The use of a multimeter determines whether the electrode has conductivity or not. If the electrode is not aligned then the tube light will not work. Replacing the tube light.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –