
Usually, any sensor is an electrical device that we use to detect as well as respond to certain types of signals like electrical or optical. The implementation of sensor techniques in voltage or current has become a good option for measuring voltage and current methods.
The advantages of sensors over the orthodox method of measurement mainly include such features as low size, low weight, high security, high accuracy, and environment friendly. In today’s article, we will see what a voltage sensor is. What are the types of voltage sensors and what are their applications we will talk about today?
Suggested Read: Different Types of Sensors used in Automobiles
What is a Voltage Sensor?

Voltage sensors are used to monitor or measure, calculate, and determine the supply of voltage. With the help of this sensor, we can determine the AC or DC voltage level. The input of this sensor can be voltage. While the output can be output switches, analog voltage signals, current signals, audible signals, etc.
Some of the sensors available in the market provide sine waveforms or pulse waveforms such as output and vibration area modulation that can generate outputs like PWM (pulse width modulation) or FM (frequency modulation). The size of this sensor depends on the mains voltage divider.
A voltage sensor is a device that can detect or sense a particular type of electrical or optical signal and also respond. Implementation of Voltage Sensor and Current Sensor technology has become the best choice for conventional current and Voltage measurement methods.
Suggested Read: What is a Motion Sensor? | Types of Motion Sensor
Types of Voltage Sensors:
There are two main types of Voltage sensors which are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types of Voltage Sensors |
| #1. | Resistive Type Sensor |
| #2. | Capacitor Type Sensor |
#1. Resistive Type Sensor:
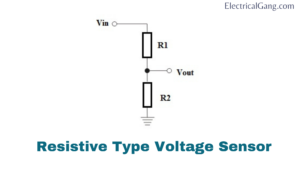
This type of sensor consists mainly of two circuits, a voltage circuit breaker, and a bridge circuit. In this circuit, the resistor acts as a sensing element. Voltage is divided into two resistors, such as a variable resistor and a reference voltage, to form the circuit of a voltage divider. Voltage supply on this circuit when applicable. This can be determined by the resistance used in the output voltage circuit. So the voltage change can be increased.
The bridge circuit can be designed with four resistors. One of these resistors can be subjected to a voltage detector device. The change in voltage can be displayed directly. This difference can be amplified alone but the difference in the Voltage separator circuit is not just extended.
Vout = (R1 / R1 + R2) * Vin
#2. Capacitor Type Sensor:
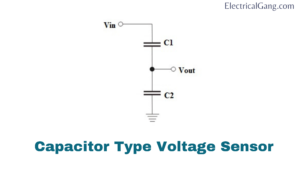
We all know that two conductor plates are used in a capacitor. The conductor is kept between these two plates. This non-conductive material is known as a dielectric. When an AC voltage is applied to this plate, the current will begin to pass due to the attraction of the electron or the interference by the voltage across the opposite plate.
The area between these two plates will become a complete AC circuit without any hardware connection. This is how a capacitor works.
Next, we can discuss the voltage split in two capacitors which are in series. Usually, a high voltage will develop in a component with a high impedance in the circuit of the series. In the case of a capacitor, the capacitance and impedance are always in opposite proportions.
The relationship between Voltage and capacitance is as follows:
Q → Charge (Coulomb).
C → Capacitance (Farad).
XC → Capacitive reactance (Ω).
f → Frequency (Hertz).
From the formula given above, we can clearly say that the smallest voltages will come together in a small capacitor. The capacitor voltage sensor works on the basis of this simple principle. Suppose we hold the sensor in our hand and then place its tip next to the live conductor.
Here we are introducing the sensory element of high impedance into a series of capacitive coupling circuits. Currently, the tip of the sensor is the smallest capacitor connected to a live voltage. Thus the whole voltage will evolve into a sensing circuit. Which can detect Voltage and turn on the buzzer or light. This is the back of the non-contact voltage sensor that you can use at home.
Suggested Read: Optical Sensor Basics | Types of Optical Sensor
Advantages of Voltage Sensors:
The advantages of Voltage sensors are as follows:
- The environment is conducive.
- Plenty of dynamic range.
- Non-satisfactory.
- Increases employee safety.
- Small in weight and size.
- The degree of accuracy is very high.
Applications of Voltage Sensors:
The application of the Voltage sensor is as follows:
- Detects power failure.
- Load sensing.
- Controls the temperature.
- Power demand control.
- Fault finding.
- Controls electricity demand.
- Safety switching.
Suggested Read: What is a Signal Isolator? | A Complete Guide
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

What is a voltage sensor?
Voltage sensors are used to monitor or measure, calculate, and determine the supply of voltage. With the help of this sensor, we can determine the AC or DC voltage level. The input of this sensor can be voltage. While the output can be output switches, analog voltage signals, current signals, audible signals, etc.
How does a voltage sensor work?
Voltage sensors are used to monitor or measure, calculate, and determine the supply of voltage. With the help of this sensor, we can determine the AC or DC voltage level. The input of this sensor can be voltage. While the output can be output switches, analog voltage signals, current signals, audible signals, etc.
What is the purpose of the voltage sensor?
A voltage sensor is a sensor used to calculate and monitor the amount of voltage in a substance. The voltage sensor can determine the AC voltage or DC voltage level.
What is the application of the Voltage sensor?
The application of the Voltage sensor is as follows:
- Detects power failure.
- Load sensing.
- Controls the temperature.
- Power demand control.
- Fault finding.
- Controls electricity demand.
- Safety switching.
What are the different types of sensors?
List of various types of sensors:
- Vision and Imaging Sensors.
- Temperature Sensors.
- Radiation Sensors.
- Position Sensors.
- Proximity Sensors.
- Pressure Sensors.
- Photoelectric Sensors.
- Particle Sensors.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –

