Hello friends, in today’s article we will see what is MOSFET, what are its types, and what are its uses. The full name of MOSFET is Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. It is a semiconductor device used for the amplification of electronic signals in electronic devices for the purpose of a switch in electronic equipment.
MOSFET is a core or integrated circuit, where it is designed and forged into a single chip because the device is available in a very small size. The discovery of MOSFET has seen new changes in the field of electronic switching.
Suggested Read: What Is Free Energy Generator? | The Complete Guide
What is MOSFET?
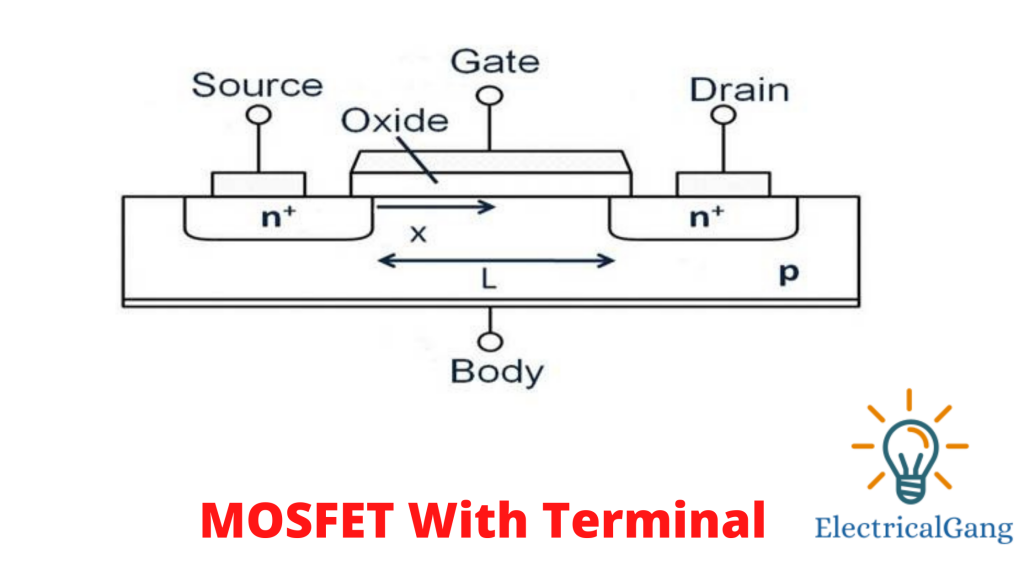
The MOSFET is a four-terminal device with source (S), gate (G), drain (D), and body (B) terminals. The main part of MOSFET is connected by the source (S). This is how the other 3 terminal devices form the field-effect transistor. MOSFET is a type of transistor used in both analog and digital circuits. This is the main introduction to MOSFET.
The general figure of MOSFET is as follows.
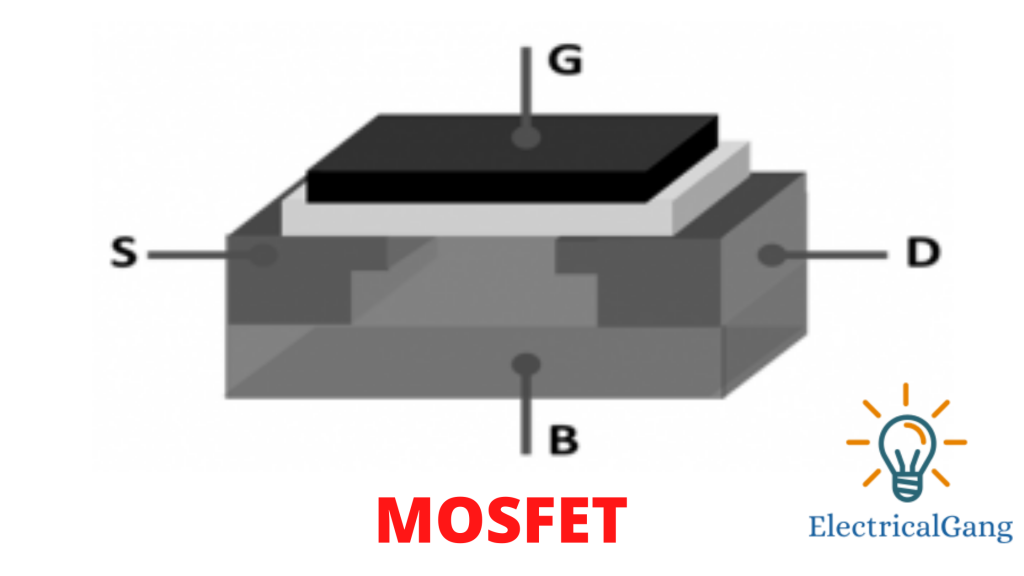
The efficiency of MOSFET as shown in the figure above depends on the electrical variation in the width of the channel with the current of the conductor (either holes or electrons). The charge carrier goes in through the source terminal and exits through the drain terminal. The width of the channel is controlled by an electrode called a gate and is located between the source and the drain.
It is insulated from a channel near an extremely thin layer of metal oxide. The MOS capability that exists in the device is the critical section where the whole operation is holistic.
Suggested Read : What Is a Terminal Block? | Types of Terminal Blocks | Advantages of Terminal Blocks
MOSFET Construction: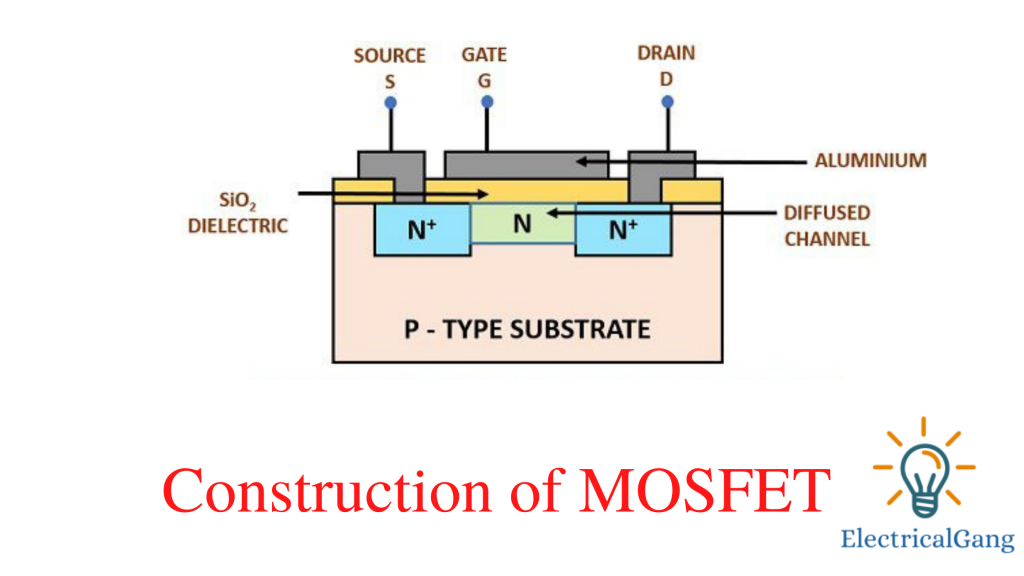
The power MOSFET is shaped like a rectangular box with a vertical 4 layers. In which the P-type layer is in the middle part as the main part. This is the n – layer exit layer which is kept slightly lower than the drain and source level. The breakdown of the power MOSFET determines the width of the voltage drift level.
Both the first and last levels are N + levels. The first layer is the source layer and the last layer is the drain layer. N + P N- N + structure word growth mode as N channel MOSFET. A P-channel MOSFET structure has the opposite doping profile. The gate terminal is not directly connected to the P-type layer but has a layer of metal oxide in between.
This layer of metal oxide acts as a dielectric layer between the metal and the semiconductor. This creates a MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) capacitance at the input of MOSFET. This capacitance is large (> 1000 pF). The oxide layer provides a good insulating property by providing a SiO2 layer that separates the gate terminal from the body layer.
Suggested Read: What is a Varactor Diode? | The Definitive Guide
Working Principle of MOSFET:
The main principle of the MOSFET device is that the voltage and current between its source and drain terminal can be easily controlled. The function of the MOSFET device is similar to that of a normal switch. The functionality of the MOSFET device depends on the capacitor of the MOS. The capacitor of MOS is an important part of MOSFET.
The semiconductor part below the metal oxide layer between the source and the drain terminal can be inverted from P-type to N-type by application with the help of positive and negative gate voltage. When we apply a positive gate voltage, the pores present below the oxide layer are pushed downwards along the substrate.
The depletion field is formed by the bound negative charge that is associated with the accepting molecules. When the time electron arrives, the channel develops. The positive voltage also attracts electrons from the N + source and drain regions in the channel.
Now if a voltage is given between the source and the drain then the current flows freely between the source and the drain and the electrons in the gate voltage channel are controlled. Instead of a positive voltage, if we apply a negative voltage, a hole channel will be created below the oxide level.
P-channel MOSFET:
Part of the P-channel lies between the source and drain of the MOSFET which has 4 terminals with terminals like gate, drain, source, and body. Drain and source are heavily doped positive fields while the body or substrate is N-type. The current is always in the direction of the positively charged hole.
When we supply voltage with negative energy at the gate terminal, the electron below the oxide layer is pushed downwards into the substrate. The depletion field is formed by the bound positive charge that is associated with the donor molecule. Negative gate voltage also attracts holes from the P + source and drain region in the channel area.
N Channel MOSFET:
The N channel is located between the source and the drain terminal in MOSFET. These are 4 terminal devices that have terminals like gate, drain, source, and body respectively. The drain and source in this type of field-effect transistor are heavily doped N + region and the substrate or body is P-type.
The current flow of this type of phosphate is caused by a negatively charged electron. By the time a positive voltage is applied to the gate terminal, the pores present under the oxide layer are pushed downwards into the substrate.
The depletion field is formed by the bound negative charge associated with the accepting molecules. Upon access to electrons, a channel is formed. The positive voltage also attracts electrons from the n + source and groove areas in the channel.
Now, if a voltage is applied between the drain and the source the current flows freely between the source and the drain and controls the electrons in the gate voltage channel. If we apply a negative voltage a hole channel will be created under the oxide layer instead of the positive voltage.
Suggested Read: Difference Between Locked Rotor Current and Starting Current
Types of MOSFET:
There are 2 types of MOSFET which are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types of MOSFET |
| #1. | Depletion Mode |
| #2. | Enhancement Mode |
#1. Depletion Mode:
The channel shows its maximum conductivity when no voltage is given at the gate terminal. As positive or negative voltage is applied to the gate terminal, its channel conductivity decreases.
#2. Enhancement Mode:
When there is no voltage at the gate terminal, then the device does not operate. When there is a maximum voltage above the gate terminal, the device exhibits extended conductivity.
Application of Power MOSFET:
- This is used for motion control of a DC motor.
- Because the speed of the motor can be increased with the help of switching, it is suitable for the construction of chopper amplifiers.
- Functions as passive components for various electronic elements.
- As a relay driver.
- As a display driver.
- In the power amplifier.
- In high-frequency inverter.
- Uninterrupted Power Supplies (UPS).
- Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS).
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –