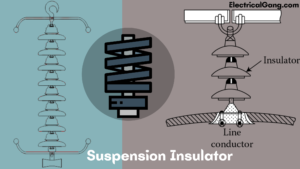
Electrical insulators work to resist the flow of electrical current and work on the principle of resilience to protect the electrical device from short circuits. Some of the best examples of insulators are wood, plastic, and polymer. Insulators are mainly used for large overhead transmission lines. Whose function is supported by poles or towers to prevent leakage of currents? Many types of insulators are used in the transmission line such as pin type, suspension type, post type, strain type, spool-type, ceramic type, non-ceramic type, etc.
Today we will see in today article on what is a suspension-type insulator. In today’s article, we will see detailed information like what is Suspension Insulator Construction and Working and how many types there are.
Suggested Read: Types of Electrical Insulator in Transmission (Overhead) Lines
What is Suspension Insulator?
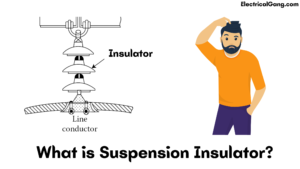
This type of insulator also acts as a conductor to protect the overhead transmission line. Porcelain material is commonly used in the manufacture of insulators. This includes a string of single or insulating discs hanging on the tower. This insulator operates at 33KV and removes the boundary of the pin-type insulator shown below.
- The size and weight of this insulator are more than 33KV.
- Replacing a bad or damaged insulator is expensive.
- Unit insulators are difficult to handle and replace.
Properties of Insulator Material:
Any insulating material must have the following properties:
- It must be mechanically strong.
- Electrical insulation resistance must be high.
- Changes in the environment should not affect the physical and electrical properties of the insulator.
- The dielectric strength of the material must withstand high-voltage stresses
- The material should be free from impurities. There should be no cracks and non-porous.
- The safety factor should be taken into account.
Suspension Insulator Construction and Working:
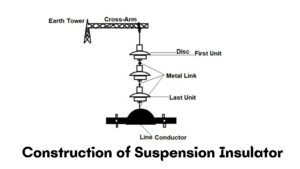
Image Credit: www.elprocus.com
The suspension insulator consists mainly of two parts one is the cross arm and the other is the insulator which we also know as the disc insulator. With the number of Metalink links. Suspension insulators or suspension strings are developed by attaching a number of closed insulators in series using metallic links. In which the conductor is suspended by the lowest insulator and the top of the insulator is protected by a cross arm. This type of insulator is specially used for overhead transmission lines.
Suggested Read: What are Conductors and Insulators | Examples Of Conductors and Insulators
String Efficiency Derivation:
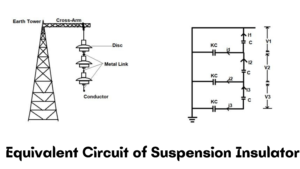
Image Credit: www.elprocus.com
The string efficiency of the suspension insulator can be obtained using the figure below. It consists of three-disc string suspension insulators with a metallic link between them to create a capacitive effect between them. This effect can be self-capacitive or mutual capacitive. Assume that shunt capacitance = self-capacitance. The current in each disk varies due to the presence of shunt capacitance.
Applying Kirchhoff’s law to Nord ‘A’
Where I1, I3, I2 and i1, i2, i3 = current flow in the conductor,
V1, V2, V3 = voltage
K = Constant
ω = 2πf
I2 = I1 + i1 V2Ωc = V1ωC+V1ωkC V2 = V1 +V1k V2 = (1 + k) V1 ……………… 1
Applying Kirchhoff’s law to Nord ‘B’
I3 = I2 + i2 V3ωC = V2ωC + (V2 + V1) ωkC V3 = V2 + (V1 + V2) k V3 = kV1 + (1 + k) V2 V3 = kV1 + (1 + k) 2 V1 (From 1) V3 = V1 [k + (1 + k) 2] V3 = V1 [k + 1 + 2k + k2] V3 = V1 (1 + 3k + k2) ……… (3)
Is the voltage between the conductor and the earth tower,
V = V1 + V2 + V3 V = V1 + (1 + k) V1 + V1 (1 + 3k + k2) V = V1 (3 + 4k + k2) ……… (4)
From the above equation, we can say that the voltage at the top disc is the minimum while the voltage at the lowest disc is the maximum. Therefore the unit closest to the conductor experiences maximum electrical stress which can also cause a puncture. It is represented as a string efficiency ratio.
String Efficiency = String Voltage / (Number of Discs x The Conductor Voltage)
The efficiency here is directly proportional to the uniform distribution of voltages. The efficiency in an ideal test is 100%. If the voltage across each disk is distributed evenly and that is not practically possible. It would be more advisable to use a shorter string in the insulator than a larger string to achieve 100% efficiency.
Sugested Read: Difference Between Transmission Line And Distribution Line
Types of Suspension Insulators:
Suspension insulators are divided into two main types as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types of Suspension Insulators |
| #1 | Cap-and-Pin Type |
| #2 | Interlink Type |
#1. Cap-and-Pin Type:
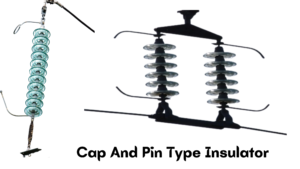
These types of insulators include forged steel caps and forged steel pins attached to porcelain. These units are connected either by socket and ball or by pin-cleavage connections.
#2. Interlink Type:
This type of insulator is also known as a Hewlett-type insulator. Porcelain is used in interlink-type insulators. This porcelain consists of two curved channels at 90 degrees. In which a U-shaped steel link passes through this channel connecting the unit.
The interlink type insulator is mechanically stronger than the Cap-and-Pin Type. The main advantage of both of these is that the porcelain continues to support the metallic link even if it is broken. This way the power supply is not interrupted. The disadvantage is experiencing high electric stress.
Advantages of Suspension Type Insulator:
The advantages of suspension insulators are as follows:
- This insulator is highly flexible.
- The cost of this insulator remains low.
- The string is free to swing in any direction and so there is flexibility for the transmission line.
- If one unit in the entire series goes bad, it can be easily replaced with a new unit without having to replace the entire string.
- Each unit can operate at a voltage of approximately 11kV and is therefore connected in series with a series of discs in the appropriate number depending on the suitability of the voltage.
Disadvantages of Suspension Type Insulator:
The disadvantages of suspension insulators are as follows:
- The cost of this insulator is higher compared to pin-type and post-type insulators.
- The distance between the two conductors is greater.
- The height of the transmission tower is higher.
Applications of Suspension Type Insulator:
The application of suspension insulator is as follows:
- These insulators are mostly used in areas where high voltage is required.
- Transformers.
- Electric motors.
- Railway lines.
- Generator.
- Electric poles, etc.
Most Commonly Asked Questions:

What is the use of a suspension insulator?
The main function of a suspension insulator is to support the transmission line on the tower. Which separates the transmission line from the tower. It plays an important role in the safe supply of electricity. Suspension insulators are used in two or more configurations depending on the transmission voltage and the consumption environment.
What are the main advantages of suspension insulators?
The advantages of suspension insulators are as follows:
- This insulator is highly flexible.
- The cost of this insulator remains low.
- The string is free to swing in any direction and so there is flexibility for the transmission line.
- If one unit in the entire series goes bad, it can be easily replaced with a new unit without having to replace the entire string.
What insulators are used in transmission lines?
There are mainly 5 types of insulators used in the transmission line as overhead insulation as follows:
- Pin insulator.
- Stay Insulator.
- Shackle Insulator.
- Suspension insulator.
- Strain insulator.
Where are the suspension insulators mainly used?
The main advantage of this insulator is that it uses less voltage and is extremely flexible. Such insulators are mainly found easily in the railway lines, head poles, etc.
What is the best insulator?
The best insulator is a Vacuum.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –
Thanks so much