
Resistors are commonly used in every electronic device. The main function of a resistor is to maintain a fixed value of voltage and current in an electronic circuit. The resistor works on the principle of Ohm’s law. And as a rule, the voltage across the terminals of a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. The unit of resistance is the ohm.
In today’s article, we will talk about what a resistor is, how many types it is, and why it is calculated and we will see all the information about it in today’s article.
What is an Electrical Resistor?
A resistor is nothing but an inert component in an electronic circuit that resists current. There are many different types of resistors. Resistances vary in their construction, power dissipation capacity, and tolerance to various parameters (e.g. temperature and light).
Different Types of Resistors:
There are many types of resisters available in the market which are categorized on the basis of rating and size as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types of Resistors |
| #1. | Wire Wound Resistors |
| #2. | Metal Film Resistors |
| #3. | Thick Film and Thin-Film Resistors |
| #4. | Network and Surface Mount Resistors |
| #5. | Variable Resistors |
| #6. | Special Resistors |
#1. Wire Wound Resistors:
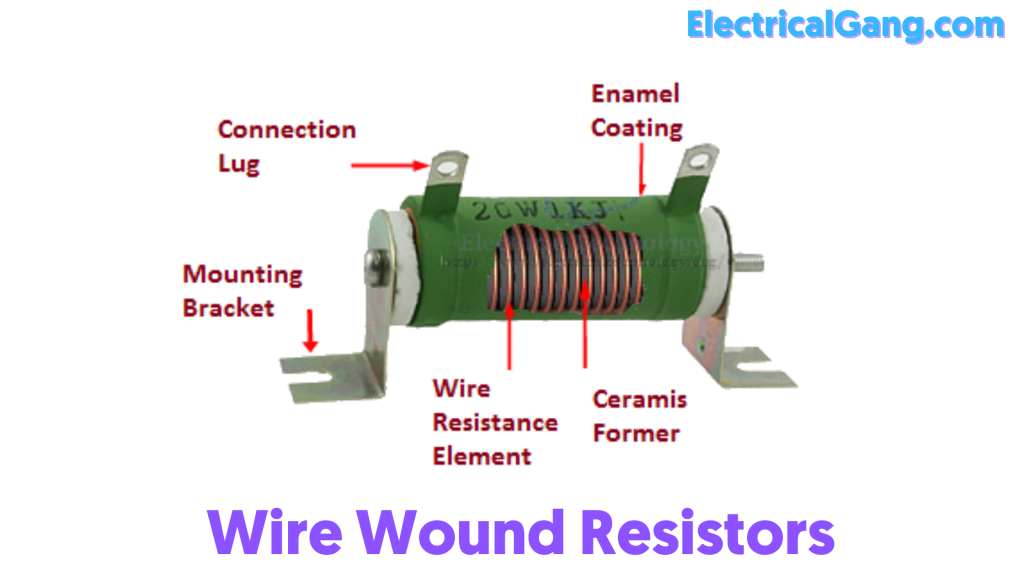
Wire wound resistors are made by wrapping the resistive wire around the insulating core. Resistance wires are usually tungsten, manganin, nichrome or nickel, or nickel-chromium alloys. And the insulating core is made from tool materials like porcelain, backlight, and press bond paper.
Manganin Wire-wound Resistors are very expensive and are used in very sensitive areas. Wire wound resistors are calculated in the oldest resistors. It has properties like high power ratings and low resistance values. It can be used very hot so it is kept in a fine metal case.
Advantages of Wire-wound Resistors:
The advantages of wire wound resistors are as follows:
- Such resistors make less noise compared to carbon composition resistors.
- Works well in overload situations.
- It is reliable and flexible.
- This is used with DC and the Audio frequency range.
The Disadvantage of Wire-wound Resistors:
The disadvantages of wire wound resistors are as follows:
- The cost is too high.
- This is not used in high-frequency equipment.
Suggested Read: What Is Ripple Factor | Ripple Factor Calculation
#2. Metal Film Resistors:
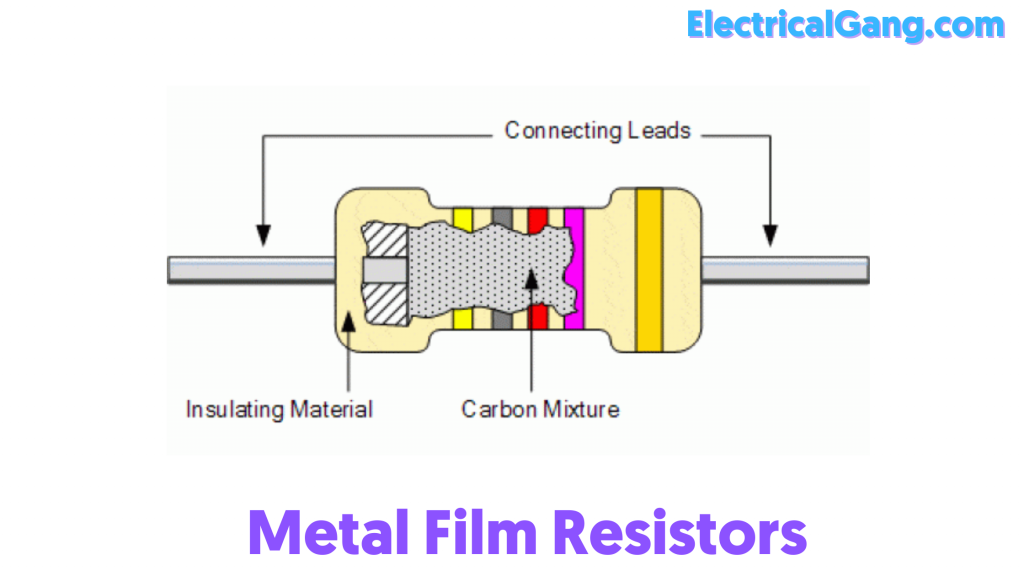
The construction of metal film resistors and carbon-film resistors is similar. Both are made of metal oxide or a small rod of ceramic-coated metal. The basis of its resistivity is controlled by the thickness of its coating layer. This resistor has properties like reliability, accuracy, and stability. These resistors are easily found in different resistance values. This is used in places where stability and noise levels are important.
#3. Thick Film and Thin-Film Resistors:

Thin film resistors are made by sputtering some resistive material on the insulating vacuum deployment method and hence this system becomes more expensive than thick film resistors. The resistive element in this resistor is about 1000 agrostams. Thin-film resistors have a better temperature coefficient, lower capacitance, less parasitic induction, and less noise.
This resistance is selected for active and passive components of electricity such as microwave power termination, microwave power resistors, and microwave power attenuators. It is used for applications that require high accuracy and high stability.
In the manufacture of thick film resistors, a mixture of ceramics with power glass is used. These films have a tolerance of 1 to 2%. Compared to a thin film, the thick film-resistant element is thousands of times thicker.
#4. Surface Mount Resistors:
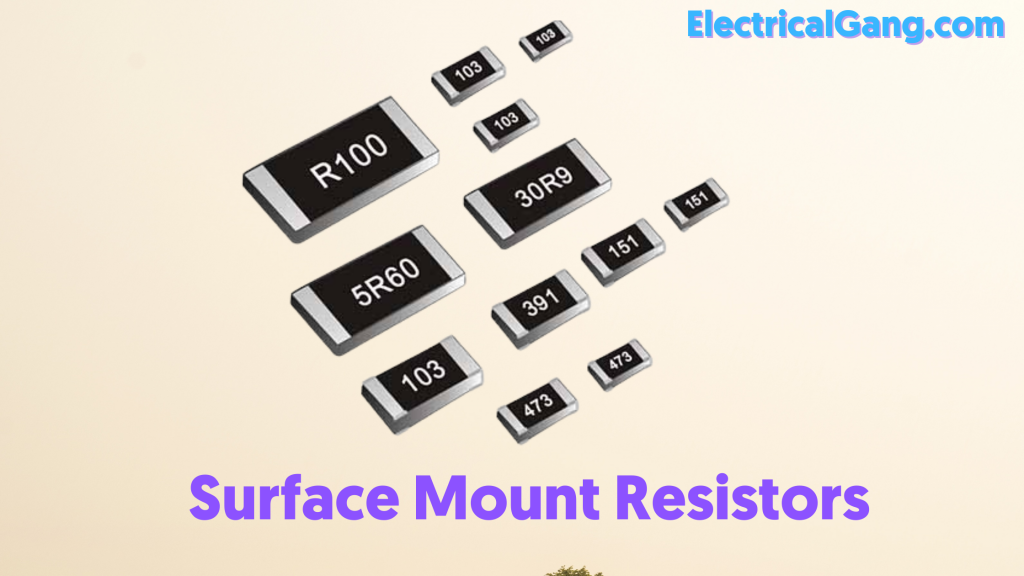
Surface Mount Resistors come in different packages and shapes. Which has been approved by the Electronics Industry Alliance. This resistor is made by depositing a film. Due to its small size, it does not have enough space for color-code bands.
The tolerance of this resistor is as low as 0.02%. There are 3 to 4 characters in the form of this identity. The size of the 0201 resistors is the smallest. Whose resistance is 0.60 mm x 0.30 mm and these three number codes act similarly to the color code band on the wire-end resistor.
Suggested Read: What is the Voltage Divider Rule? | Voltage Divider Calculation
#5. Network Resistors:
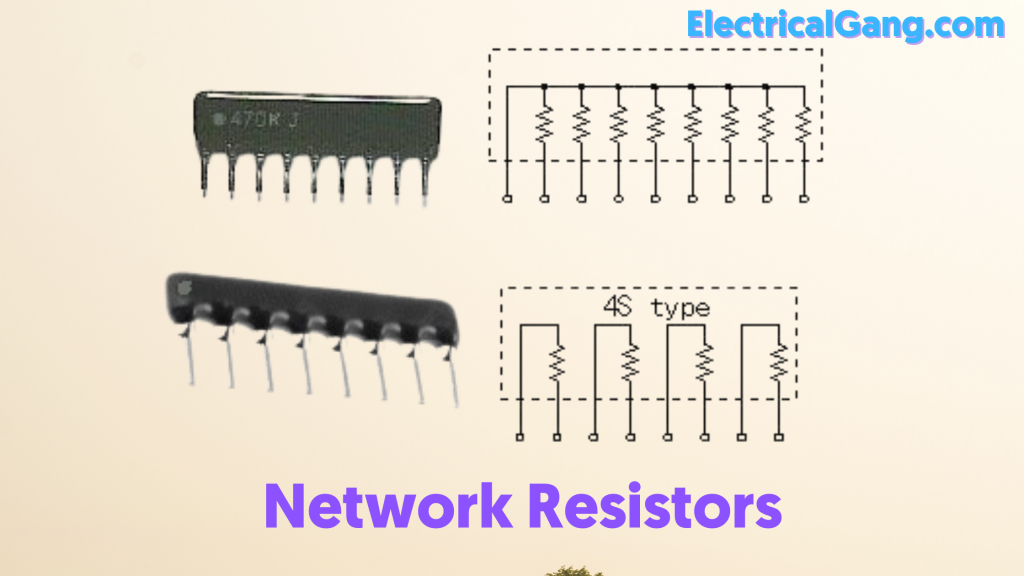
Network Resistors are a combination of resistors that give the same value to each pin. These resistors come in dual in-line and single inline packages. This resistor is used for analog to digital converters.
#6. Variable Resistors:
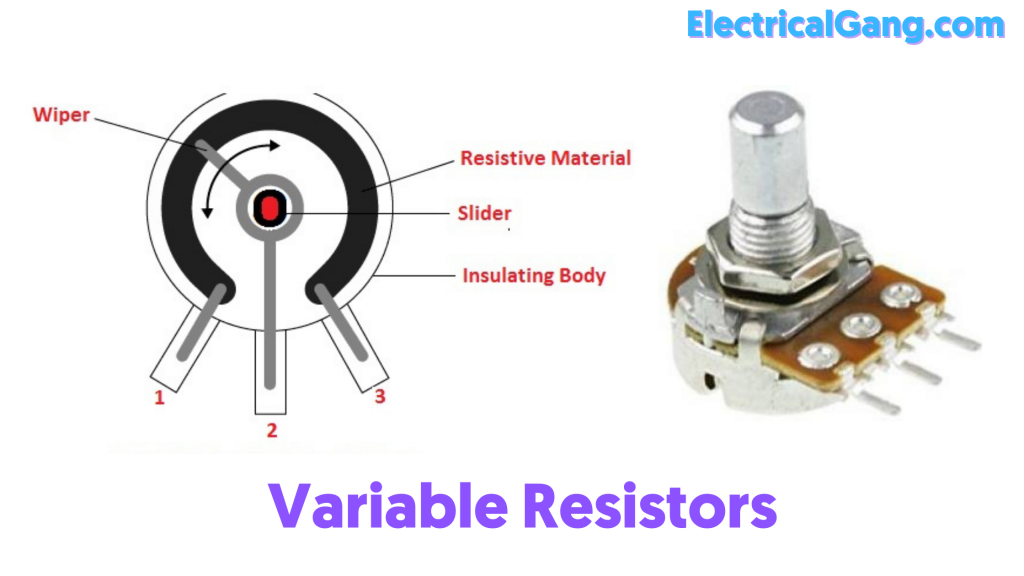
Variable Resistors are the most widely used resistors in the market. Inside this resistor, there is a fixed value of the resistance between the two terminals. This resistor is mostly used to set the sensitivity of the sensor and the voltage section. Resistance can be set more or less with the help of a viper.
Inside this resistor are three tabs with the viper in the middle. This acts to divide the voltage when all three tabs are used. It acts as a variable resistor when any other tab is used along with the intermediate tab. It acts as a fixed resistor when only one tab is used.
There are three main types of variable resistors which are as follows:
- Potentiometers.
- Rheostats.
- Trimmers.
#6.1. Potentiometers:
Potentiometers are thus three-terminal devices through which the voltage across the circuit is controlled. The resistance of both terminals is constant. While the resistance of the intermediate term is variable. Which is connected to the viper. The value of resistance can be changed by turning the wiper. It is available for up to 10 megohms.
#6.2. Rheostats:
This device has two or three terminals. This device is used for current control with the help of manual or manual. Other resistors of this resistor are also known as taped resistors or variable wire wound resistors.
In the fabrication of this resistor, the wire is made to wind the nichrome resistance around the ceramic core then it is fixed in a protective cover. The metal band is wrapped around the resistor element and used as Potentiometer or rheostats
The range of wire wound resistors ranges from 1 ohm to 150 ohms. The power rating of this resistor ranges from 3 watts to 200 watts. Depending on the power rating, the most widely used rheostats are between 5 and 50 watts.
#6.3. Trimmers:
For better efficiency and easier operation, there is an extra screw with a potentiometer or variable resistors which we call Trimmers. The resistance value can be changed by operating it with the help of a small screwdriver.
Trimmers are made of carbon film, carbon composition, cermet, and wire materials. Trimmers range from 50 Ohms up to 5 megaohms. The power rating of Trimmers potentiometers is from 1/3 to ¾ Watt.
Suggested Read: What Is a Motor Starter? | Types of Motor Starters
Special Types of Resistors:
These resistors are classified into eight sections. These are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Special Types of Resistors |
| #1. | Thermistors |
| #2. | Light-dependent Resistors (LDR) |
| #3. | Fixed Resistors |
| #4. | Varistors |
| #5. | Magneto-resistors |
| #6. | Film Type Resistor |
| #7. | Carbon Film Resistor |
| #8. | Carbon Composition Resistor |
#1. Thermistors:
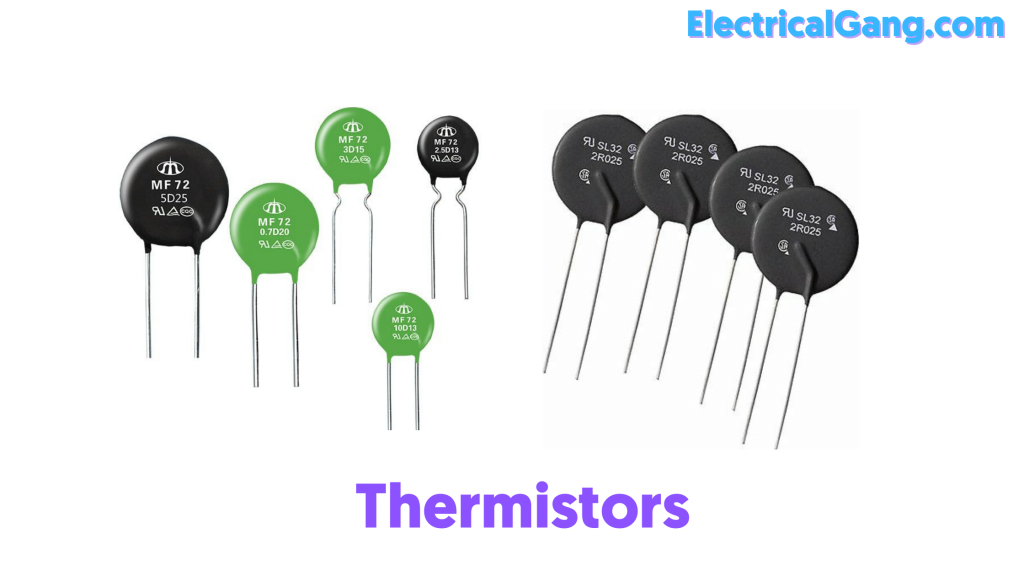

Thermistors are two-terminal devices that are very sensitive to temperature. To put it another way, it is nothing but a variable resistor. Which takes into account changes in temperature. It is made of metal oxides of thermistor cobalt, nickel, strontium, and manganese. The resistance of thermistors is proportional to the temperature.
#2. Light-dependent Resistors (LDR):
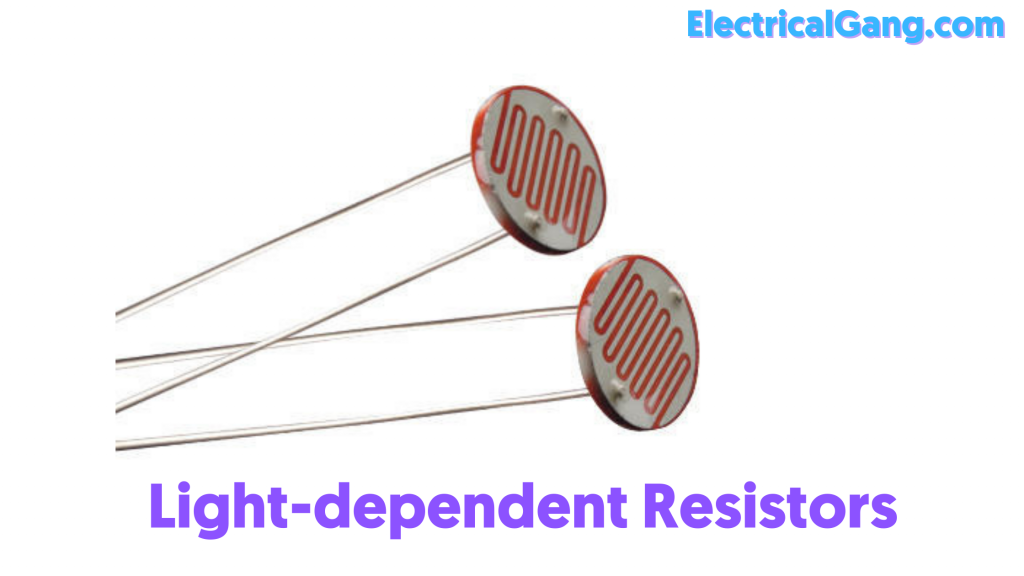
These resistors are used in many different electronic circuits. This is especially true of clocks, street lights, and alarms. Cadmium sulfide is used in its manufacture. This resistance is very high when the resistor is in the dark. When light falls on it, its resistance decreases. Electrons continue to flow and conductivity increases.
This type of resistor is available in different shapes and colors. Depending on the ambient light, this resistor is used to turn devices on or off.
Suggested Read: Transformer Designing | The Definitive Guide
#3. Fixed Resistors:
Fixed resistors are said to have no change in voltage or temperature. Fixed resistors are available in various shapes. The function of this resistor is to provide stable resistance to any situation. When any other resistor changes with increasing or decreasing temperature. Fixed resistor resistance values used in most applications are 10Ω, 100Ω, 10K, and 100K.
This is more expensive than other resistances. Since we want to change the resistance of any resistor, we need to buy a new resistor. In this case, it is different as fixed resistors can be used with different resistance values. We have the resistance of a fixed register we can easily measure with the help of an ammeter. This register has two terminals. This is used to connect other types of components in the circuit.
#4. Varistors:
When the resistance of the resistance can be changed based on the applied voltage it is known as Varistors. This is used to eliminate high-voltage transitions. In other words, it is used to protect the circuit from fatal voltage spikes.
When the voltage in a connected sensor device or system increases (due to lighting or line faults), it lowers the voltage level to a safe level i.e. it changes the voltage level to a safe level.
#5. Magneto-resistors:
The time when the magnetic field from outside is applied and the electrical resistance of the resistance changes is known as the magneto resistor. Inside this resistor is a variable resistor that depends on the strength of the magnetic field.
Another name for this resistor is MDR (Magnetic Dependent Resistor). The main purpose of this resistor is to measure the presence, direction, and strength of a magnetic field.
#6. Film Type Resistor:
Film Type Resistor consists of three types of resistors such as carbon, metal, and metal oxide. Such resistance is usually designed on insulated ceramic rods or substrates with the deposition of pure metals such as nickel, or oxide film such as tin oxide.
The resistance value of this resistor can also be controlled by increasing the width of the deposited film hence it is also known as a thick-film or thin-film resistor.
Suggested Read: What is Chemical Earthing? | A Complete Guide
#7. Carbon Film Resistor:
Such type resistors are included in fixed-type resistors. As the flow can be controlled using carbon film. Such resistors are often used in circuits. The design of this resistor includes a carbon layer or carbon film on the ceramic substrate. In this, the carbon filament acts as a resistor to the electric current.
That is why the carbon film will block the current to a small extent while the ceramic substrate acts as an insulator towards electricity. Therefore, the ceramic substrate is not allowed to heat during that. Thus, this type of resistor can withstand high temperatures without any damage.
#8. Carbon Composition Resistor:

Carbon Composition Resistor is another name for Carbon Resistor. This resistor is used in different places. Because the design is simple and the cost is low. The design is typically designed with a carbon clay cover covered by a plastic container. Resistor leads can also be made of tinned copper material.
These resistors are available in various values ranging from 1 Ω to 22 Mega. This is why it is considered suitable for Arduino starter kits. The main drawback of this resistor is that it is extremely sensitive to temperature. The tolerance range for this resistor ranges from 5 to 20%.
Due to the electric current flowing from one particle of carbon to another, this resistor makes a slight noise. So it is used in places where low-cost circuits are to be made. These resistors are available in different color bands which are used to find the resistance value of the resistor with tolerance.
Types of Resistors Color Code Calculation:
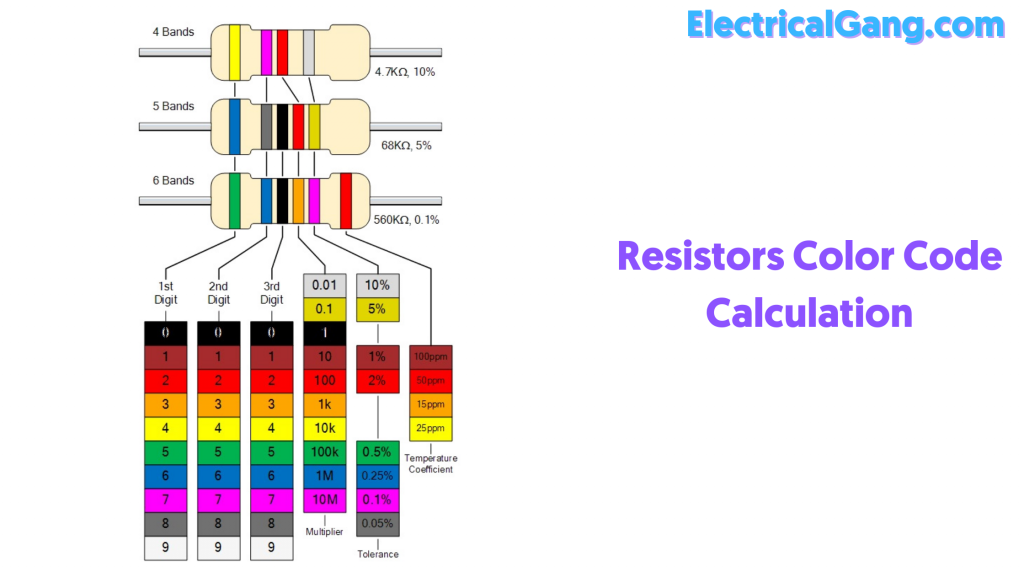
All friends have to memorize this simple sentence to find the color code of the resistor. Any resistor can be easily calculated. B B Roy of Great Bombay Via Goa to West Bengal This sequence helps to find the resistor value by looking at the colors on the color code resistors.
4 Bands Resistor Color Code Calculation:
- In the above 4 band resistors:
- Indicates the first digit or band, which is the first significant figure of the component.
- The second figure indicates the second significance of the component.
- The third digit indicates decimal multiplication.
- The fourth digit indicates the tolerance of the value in percentages.
- To calculate the color code of the above 4 band resistors,
- 4-band resistors have colors: yellow, violet, orange, and silver.
- Yellow-4, Violet-7, Orange-3, Silver-10% based on BBRBVVW
- The color code value of the above resistor is 47 × 103 = 4.7 kg ohms, 10%.
5 Bands Resistor Color Code Calculation:
- In the 5 band resistors shown above, the first three colors indicate significant values, and the fourth and fifth colors indicate multiplication and tolerance values.
- To calculate the color code of the 5 band resistors shown above, the 5 band resistors include colors: blue, gray, black, orange, and gold.
- Blue-6, Gray-8, Black-0, Orange-3, Gold-5%
- The color code value of the resistor shown above is 68 × 103 = 6.8 kg ohms, 5%.
6 Bands Resistor Color Code Calculation:
- In the 6-band resistor shown above, the first three colors display specific values; The fourth color indicates the factor of multiplication, the fifth color indicates tolerance and the sixth indicates TCR.
- To calculate the color code of the 6 color-band resistors shown above, The colors in the 6-band resistor include something like this: green, blue, black, yellow, gold, and orange.
- Green-5, Blue-6, Black-0, Yellow-4, Orange-3.
- The color code value of the above resistor is 56 × 104 = 560 kg ohms, 5%.
Application of Resistors:
The application of resistors is as follows:
- In the laboratory.
- As a shunt in ampere meters.
- To control the temperature.
- To control the voltage drop.
- In electronic circuits.
- As a multiplier in a voltmeter.
- In household appliances such as heaters, irons, immersion, etc.
- To convert electrical energy radiation in the form of heat energy radiation.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –