
Hello friends, in today’s article we talked about the Conservator Tank of Transformers From power generation to the distribution of electricity, transformers are a very essential device. Transformers are widely used in power plants and various industries. Transformers are classified based on their various uses. Different types of accessories are used in conjunction with the transformer for its long life.
Different accessories such as a breather from the transformer, a conservator tank to store the oil after it is hit, and an explosion as a safety feature. The vent conservator tank plays an important role in the auxiliary transformer.
This tank is connected to the transformer at the top so that there is enough space to spread the oil from the transformer. Once the transformer is heated the oil starts to be stored in the tank fitted in the upper part of it so it acts as a reservoir for the expanded oil in the transformer oil. In today’s article, we will discuss in detail what are a conservator tank, its construction, operation, and its types.
Suggested Read: What Is an Oil Circuit Breaker? | A Complete Guide
What is a Conservator Tank?

The Conservator Tank is simply a tank that is used to provide enough space for the oil in the transformer to spread after heating. It is placed on the roof of the transformer. The main function of the Conservator Tank is that once the transformer is loaded, its temperature rises, and the oil in it starts spreading. That is why the Conservator Tank acts like a pond for the insulation of the transformer.
Construction of Conservator Tank
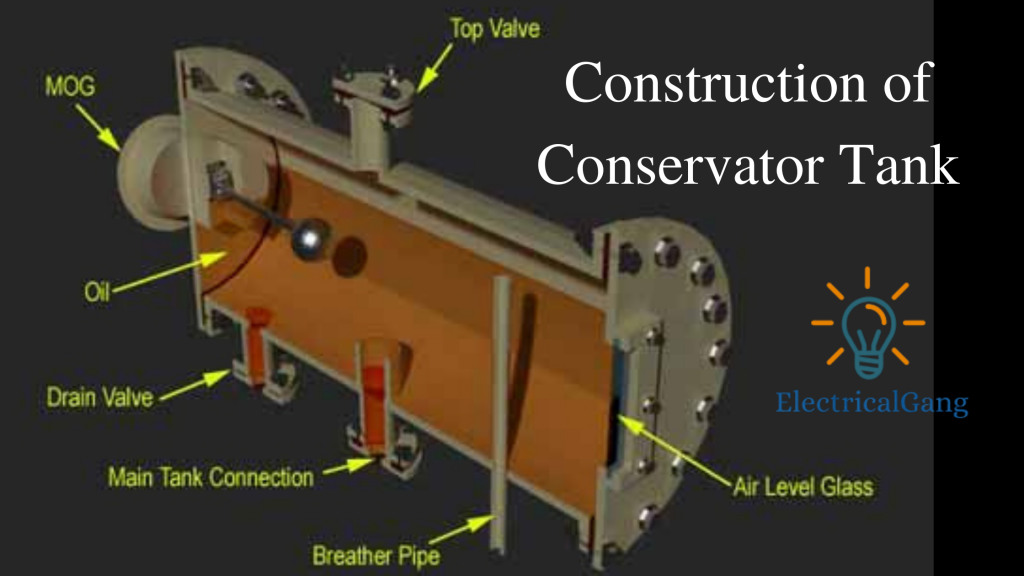
The shape of the Conservator Tank is cylindrical. The ends of the tank are airtightly closed. A large cover is placed on one side of the tank for periodic cleaning and maintenance. The pipe of the conservator tank is connected to the main tank of the transformer.
The pipe is connected to the bottom of the Conservator Tank. In the tank, a cap is attached to the top of the pipe so that any kind of oil waste does not enter the main tank from the Conservator Tank. A breather is applied to the breathing of the transformer with the help of the upper part of the Conservator Tank.
With the help of a breather, the silica gel goes through the fixed pipe to the Conservator Tank. When this pipe goes through the base, it should be well estimated at the top of the oil level in the tank. This adjustment ensures that the transformer oil does not inhale silica gel even at the maximum operating level.
Suggested Read: What Is Solar Cell? | A Complete Guide
Working Principle of Conservator Tank
The work of the Conservator Tank starts to heat up once due to the load of the insulating oil transformer and leaves in the tank facing upwards. As a result, the same amount of air in that distance is moved away with the help of breathing. As the load on the transformer decreases, the transformer cools down and shuts down.
The oil in the conservator tank seems to shrink after the atmosphere cools down. The main cause of oil shrinkage is the outside air that enters the tank with the help of silicate gel.
Types of Conservator Tank
There are two types of transformer conservator tanks which are as follows:
| Sr. No. | Types Of Conservator Tank |
| #1 | Atmoseal Type Conservator |
| #2 | Diaphragm Sealed Conservator |
#1. Atmoseal Type Conservator
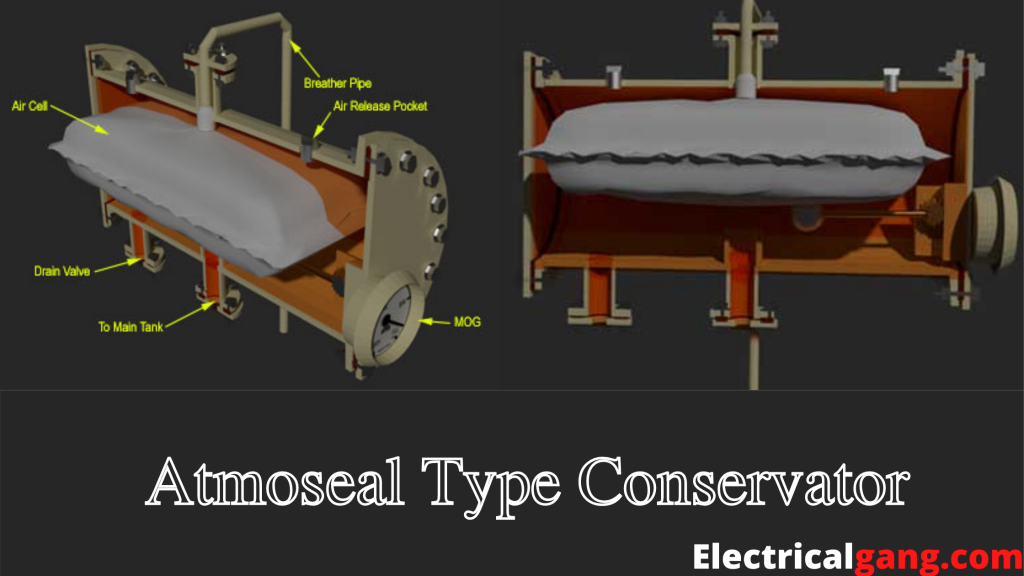
The Atomosal Conservator consists of an air cell made from the material of the NBR. This material is attached to the reservoir of the conservatory so that the silica gel breath can attach to the apex of the air cell. The oil level in the transformer will be increased and also reduced depending on the reflecting and deflecting of the air cell.
Once the air cell deflates, then the air in the air cell comes out with the help of its breath. And if this cell swells in the form of an alternative, the air from outside enters inside in the form of breath.
This design is done in such a way that the oil and air do not mix, which increases the oil life The increased space inside the tank and outside the cell can be filled with air. Air vents are provided in the upper part of the tank to expel the air from the outside of the air cell. The force inside the air cell must be maintained at 1.0 PSI.
Suggested Read: Buchholz Relay in Transformers | The Definitive Guide
#2. Diaphragm Sealed Conservator
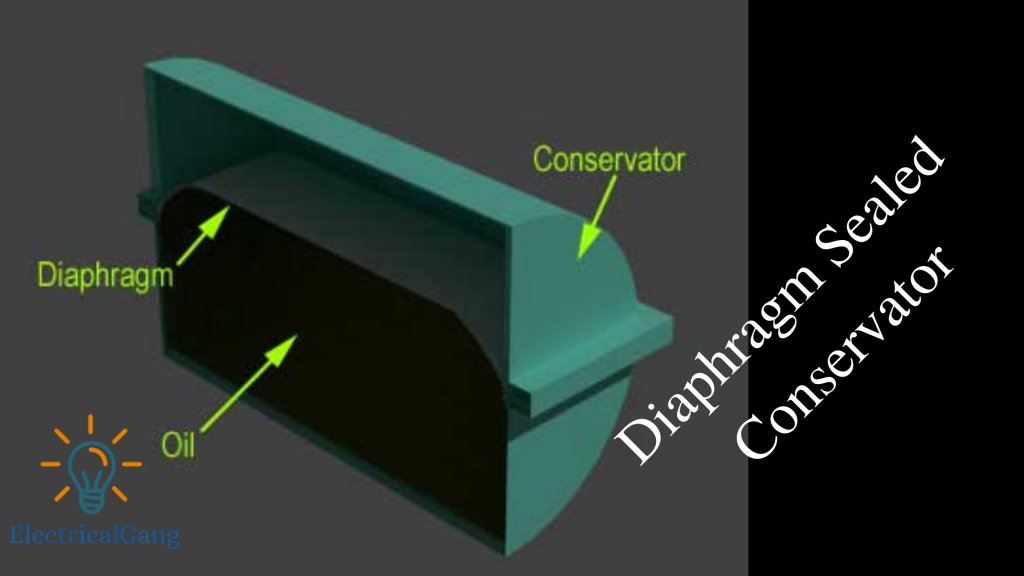
This type of seal acts as a barrier between the conservator’s outside air as well as the transformer. In such a situation the conservator tank of the transformer can be designed with two hemispherical parts.
The diaphragm inside the tank is arranged between two bolts and a half once the level of the transformer rises it pushes over the diaphragm That is why the diaphragm is used to know the level of oil in the transformer. Whenever the level of oil inside the conservator decreases, the diaphragm will deform and its empty space will be filled with atmospheric air.
This air-silica gel can be sucked during breathing. This can be connected to the center of the conservator tank in the transformer. The advantage of this type of conservator tank is that with an air cell-type conservator. If the gas is pushed to a higher level, it melts inside the transformer oil.
Over a period of time, the amount of gas in the transformer oil achieves a saturation point. In such a time, if the load of the transformer does not decrease suddenly, the temperature will drop, the transformer oil will be saturated and bubbles will develop from the gas.
If the pump is connected to a cooling circuit, then it helps to generate gas bubbles for insulation failure in the area of strong fields.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the use of the Conservator tank?
The Conservator Tank is simply a tank that is used to provide enough space for the oil in the transformer to spread after heating. It is placed on the roof of the transformer. The main function of the Conservator Tank is that once the transformer is loaded, its temperature rises, and the oil in it starts spreading. That is why the Conservator Tank acts like a pond for the insulation of the transformer.
What is the function of the breather?
The function of the breather is to prevent moisture in the atmosphere while the transformer is inhaling and to reduce maintenance costs. If it is not necessary to prevent moisture in the atmosphere in the breathing cycle of the transformer, oil can be contaminated due to its entry.
What is a transformer tank?
The transformer tank is also called the transformer tank. It is used to hold, protect, and cool the winding and core in an electrical distributor transformer. The tank body separates the oil and the core from the outside environment.
How many types of conservator tanks are there?
There are two types of transformer conservator tanks which are as follows.
- Atmoseal Type Conservator.
- Diaphragm Sealed Conservator.
Like this post? Could you share it with your friends?
Suggested Read –
very insightful, thanks so much